Respiratory diseases present a challenge for the healthcare system due to their prevalence and clinical impact. The aim of this study was to explore the current situation of hospital pharmacy in the field of respiratory diseases.
MethodObservational, cross-sectional study, with a national scope, divided into 2 parts. In an initial phase, the activity and level of pharmaceutical care in respiratory diseases was evaluated through an online questionnaire using REDCap. The survey was addressed to department chiefs and consisted of 17 items, divided into 2 modules: general data and general activity. The second phase was open to hospital pharmacists, with the aim of exploring their opinion on care, training, and improvement needs. The number of items in this phase was 19, divided into 5 modules: general data, pharmaceutical care, competencies, training, and degree of satisfaction.
ResultsIn the first phase, 23 hospitals were included. Most of them (n=20) had a pharmacist in charge of respiratory diseases. However, a large proportion of them dedicated less than 40% of their working day to this activity. The pharmacist's activity occurred at the level of external patients (n=21), hospitalised patients (n=16), and secondarily in management (n=8). Integration is greater in pathologies such as asthma, IPF, pulmonary hypertension, and bronchiectasis. Participation in committees was present in 15 hospitals, with variability in pathologies and degree of involvement. In the second phase, 164 pharmacists participated, who considered pharmaceutical care in cystic fibrosis, asthma, and lung transplant as a priority. 51% considered integration to be adequate and 91% considered it necessary to implement prioritisation criteria. Professional competencies ranged from 6.5 to 6.9 out of 10 points. Only 45% of participants had received specific training in the last 4 years, indicating greater priority for asthma, pulmonary hypertension, and IPF.
ConclusionsMost centers have pharmacists specialised in respiratory diseases. However, there is room for improvement in terms of subspecialisation, participation in multidisciplinary committees, implementation of prioritisation criteria, diversification in pathologies treated, as well as greater specific training in this area.
Las patologías respiratorias suponen un reto para el sistema sanitario por su prevalencia e impacto clínico. El objetivo del estudio fue explorar la situación actual de la labor del farmacéutico hospitalario en el campo de las patologías respiratorias.
MétodoEstudio observacional, transversal, a nivel estatal, dividido en dos partes. En la inicial se evaluó la actividad y el nivel de atención farmacéutica en patologías respiratorias mediante un cuestionario en línea con REDCap. Se dirigió a jefes de servicio y constó de 17 ítems, divididos en dos módulos: datos generales y actividad general. La segunda fase estuvo abierta a farmacéuticos hospitalarios, con la finalidad de explorar su opinión sobre la asistencia, formación y necesidades de mejora. El número de ítems del cuestionario utilizado en esta fase fue de 19, repartidos en cinco módulos: datos generales, atención farmacéutica, competencias, formación y grado de satisfacción.
ResultadosEn la primera fase participaron 23 hospitales. La mayoría (n = 20) tenían un farmacéutico responsable del área de patologías respiratorias. No obstante, gran parte de ellos dedicaba menos de un 40% de su jornada a esta actividad. La actividad del farmacéutico se produjo a nivel de pacientes externos (n = 21), ingresados (n = 16) y secundariamente en gestión (n = 8). La integración fue mayor en patologías como el asma, EPID, hipertensión pulmonar y bronquiectasias. La participación en comités bajó a 15 hospitales, con variabilidad en las patologías y el grado de implicación. En la segunda fase participaron 164 farmacéuticos, que consideraron prioritaria la atención farmacéutica en fibrosis quística, asma y trasplante pulmonar. El 51% consideró que la integración era buena y un 91% consideró necesario implementar criterios de priorización. Las competencias profesionales oscilaron entre el 6,5–6,9 sobre 10 puntos. Solo un 45% de los participantes había recibido formación específica en los últimos cuatro años, indicando mayor prioridad al asma, hipertensión pulmonar y EPID.
ConclusionesLa mayoría de centros cuentan con farmacéuticos especializados en patologías respiratorias. Sin embargo, existe margen de mejora a nivel de subespecialización, participación en comités multidisciplinares, implantación de criterios de priorización, diversificación en patologías atendidas, así como una mayor formación específica en esta área.
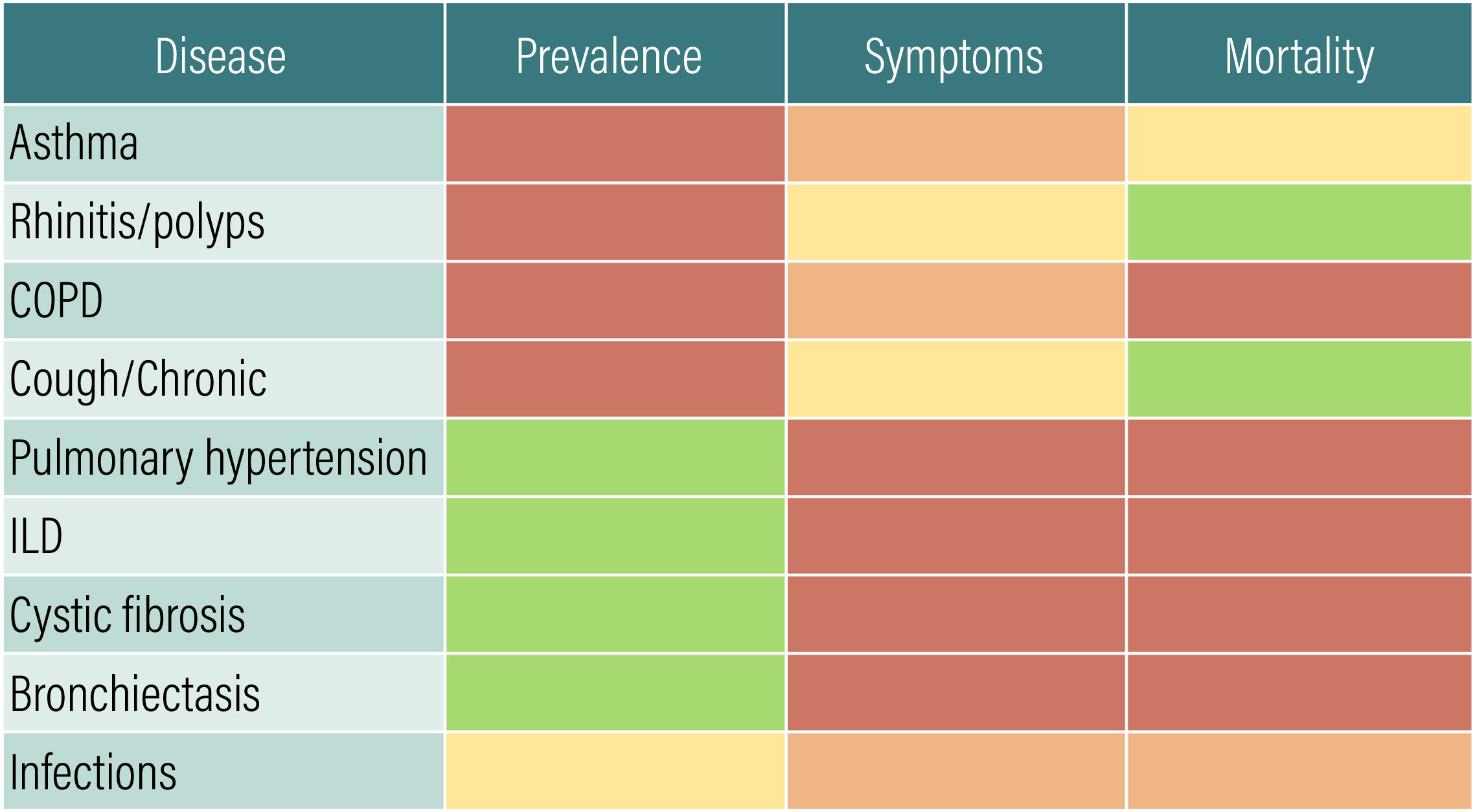
Respiratory diseases are characterised by their heterogeneity, prevalence, symptomatology, and morbidity and mortality (Fig. 1). In fact, they are the third leading cause of death worldwide and in Spain.1,2 The relevance of these diseases will increase in the future as a result of increasing prevalence, pollution, and new infections.3
Pharmaceutical care (PC) is key to the management of respiratory diseases due to complex treatments such as inhalers and nasal devices. They are used correctly only in one-third of cases due to their complexity, variability, need for coordination, lung capacity, and use of chambers, among other factors.4,5 Adherence is estimated at 50%6 and records show that only 63% of prescriptions are filled.7 Other treatments should also be taken into account, such as biologics for asthma or polyposis, and oxygen therapy for chronic obstructive respiratory disease (COPD) or interstitial lung disease (ILD).
The high prevalence of both respiratory and non-respiratory comorbidities, which lead to poorer outcomes in terms of quality of life and morbidity and mortality8–12 makes it essential to understand the complexity of these diseases, not only in terms of medications, but also in terms of the specific tests and techniques used in diagnosis and follow-up. In 2019, the Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacy (SEFH) created the Respiratory Diseases Working Group (NEUMO) to address these issues.
The aim of this article was to investigate the current situation of hospital pharmacists (HPs) in the field of respiratory disease, by delineating their healthcare activities and seeking their opinions, thereby assisting in the development of activities tailored to the identified needs.
MethodologyStudy designAn observational, cross-sectional study, in which 2 questionnaires were designed. Four experts from the NEUMO group searched various sources (Pubmed, Web of Science, Google Scholar, Google, Bing) and the grey literature, without finding any results in line with the objective of our study. Initial versions of the questionnaires were designed based on previous experiences of the SEFH in other areas and then reviewed by 10 experts from the NEUMO committee. Two further rounds of modification and revision were conducted until consensus was reached and final versions produced. The experts were experienced in questionnaire design and ensured that the thematic blocks and questions covered the most relevant aspects of the aims of this exploratory study.
Sample and proceduresIn the first phase, we used an online questionnaire via the Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) platform to assess hospital activity and PC levels in relation to respiratory diseases. Hospital pharmacy department heads were contacted via the SEFH online mailing list platform. Only one response was allowed per hospital. The survey comprised 17 items, divided into 2 modules: general data and PC (Appendix 1). It was conducted between 2 February and 13 March 2022.
The second phase was open to all HPs and sought their opinions on care, training, and needs for improvement in respiratory pathology. All members were contacted online via the SEFH mailing list. Social media was also used for communications. The REDCap platform was also used for data collection. The questionnaire used in this phase comprised 19 items divided into 5 modules (Appendix 1). It was conducted between 20 September and 1 November 2022.
Definition of variablesAppendix 1 includes the full list of variables, as well as their categorisation and scoring.
Data analysisWe performed a descriptive analysis (frequencies, percentages, range, mean, standard deviation, and confidence intervals). As this study was exploratory, no sample size was predefined. All statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS V.19.
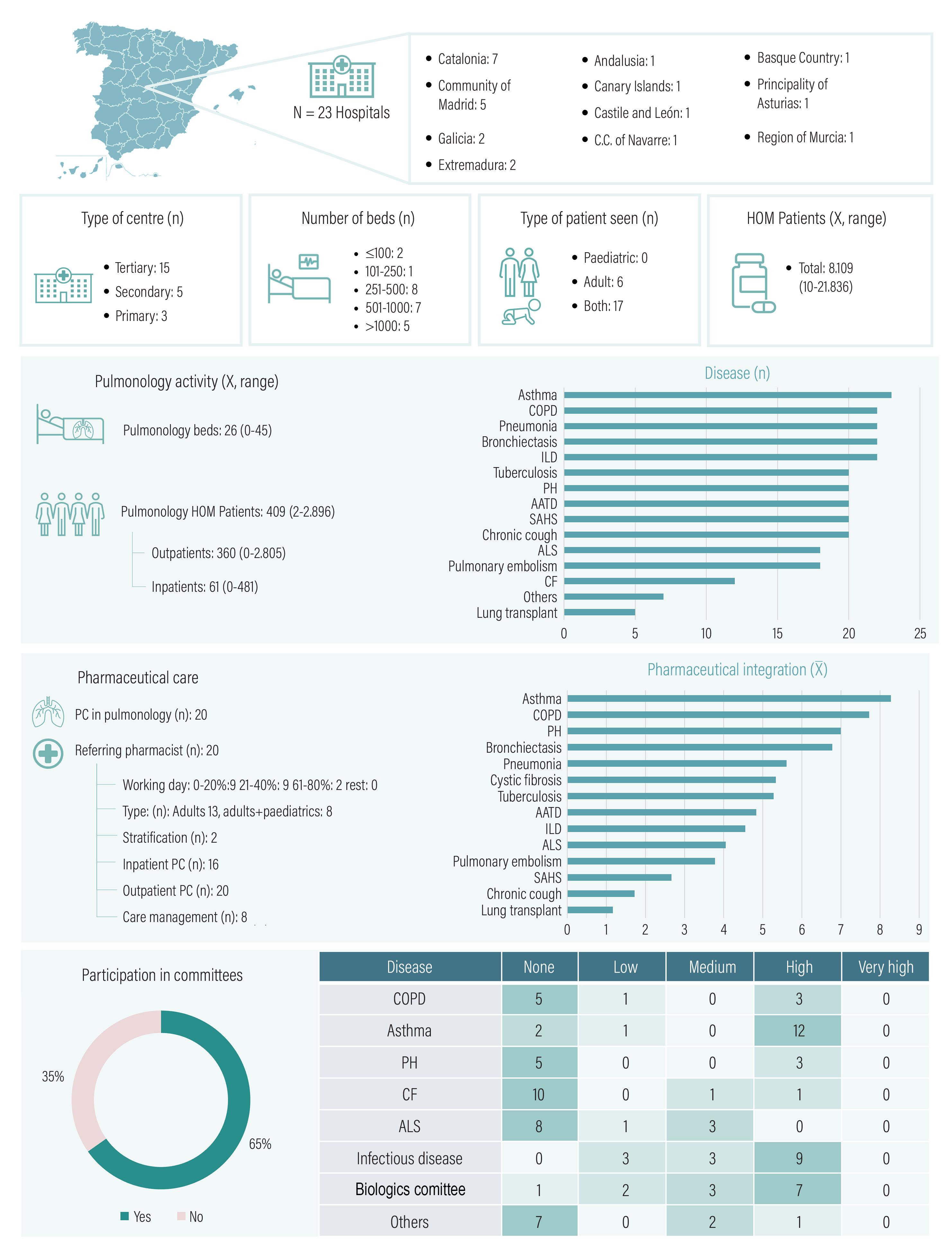
ResultsFirst surveyIn total, 23 hospitals participated, resulting in a 15% response rate out of the 157 heads of department contacted. Most of these hospitals treated both adult and paediatric patients, 12 of them had over 500 beds, and 15 of them were tertiary hospitals (Fig. 2).
Pharmaceutical care and activity in respiratory diseases.
PC, pharmaceutical care; AATD, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; ILD, interstitial lung disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CF, cystic fibrosis; PH, pulmonary hypertension; HOM, hospital outpatient medication; SAHS, sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome.
The average number of beds in pulmonology departments was 26. The average number of outpatients and inpatients was 360 and 61, respectively.
Most hospitals (n=20) had a referring pharmacist, 18 spent less than 40% of productive time in this area, and 2 had stratification tools. Most hospitals (n=20) provided PC to outpatients, 16 to inpatients, and only 8 hospitals were involved in healthcare management activity. The highest number of pharmacists were involved in the areas of asthma, ILD, pulmonary hypertension, and bronchiectasis.
Participation in committees was observed in 15 hospitals, most notably in the areas of asthma, infectious diseases, and biologics. However, participation levels were low in many cases.
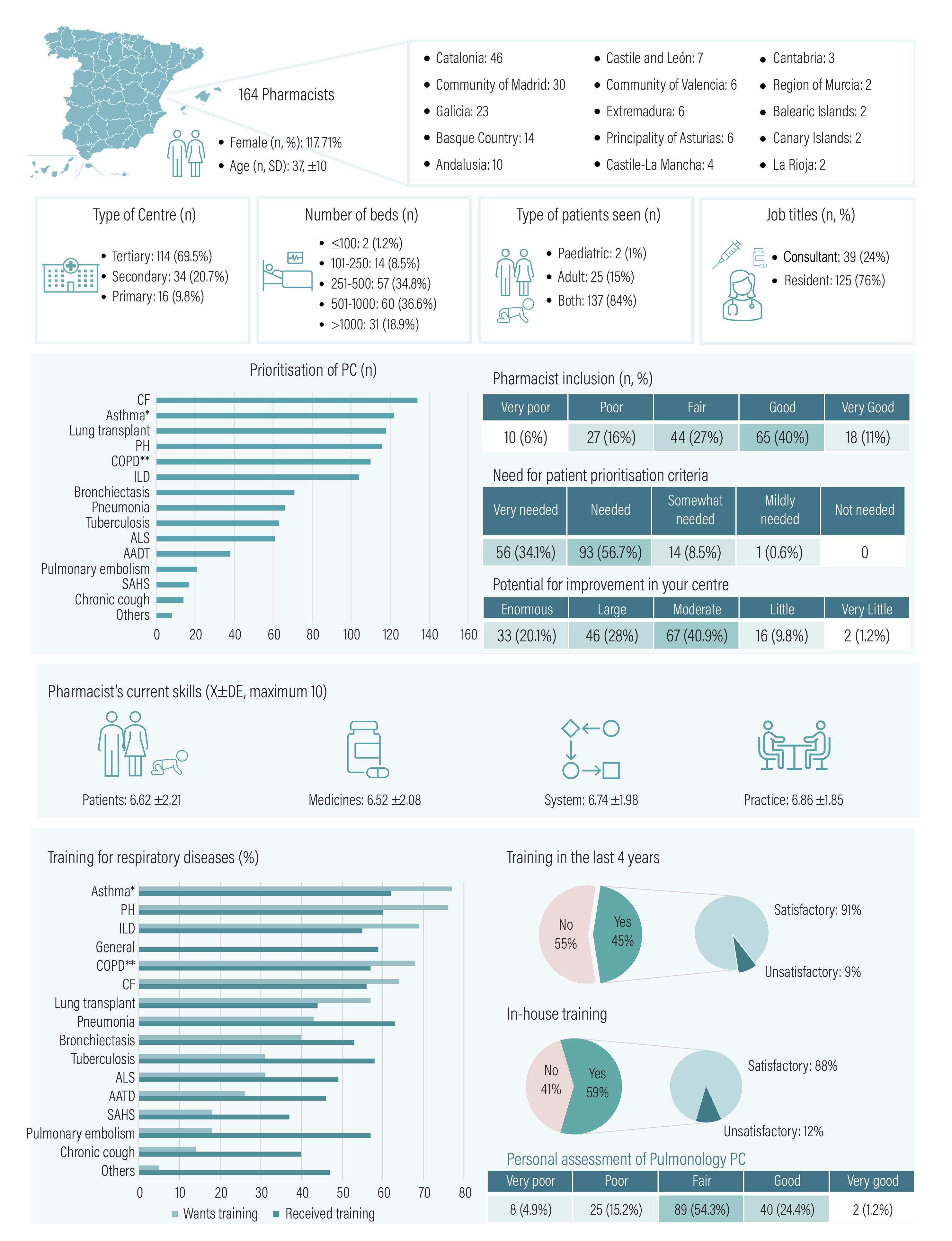
Second surveyWe received 164 responses from a potential pool of 4434 pharmacists. The average age of respondents was 37 years, of whom three-quarters were residents (Fig. 3). In addition, 69.5% worked in tertiary care hospitals, 52.2% in hospitals with more than 500 beds, and 84% provided care for both adult and paediatric patients.
Opinions on PC and respiratory disease training.
PC, Pharmaceutical care; AATD, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; ILD, interstitial lung disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; SAHS, sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome. *Includes rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. **Includes bronchitis and emphysema.
Respondents felt that PC should prioritise cystic fibrosis, asthma, and lung transplantation. Just over half (51%) rated, the inclusion of HPs in the area of respiratory disease as good/very good. The majority (90.8%) considered that prioritisation criteria were necessary/very necessary. A total of 89% suggested that the role of the HP in committees could be improved. Pharmacists' competencies showed similar scores (6.5–6.9) in all 4 areas rated.
Pharmacists felt they were better trained in the areas of pneumonia and asthma than in other diseases. Overall training in respiratory diseases was scored at 5.89±1.48. Respondents were most interested in further training in asthma, pulmonary hypertension, and ILD. Less than half of the respondents (45%) had received any training in the last 4 years and 59% had annual training sessions in their hospital. Most respondents found the training to be satisfactory.
More than half of the respondents rated their own knowledge and skills related to PC in respiratory disease as fair (54.3%).
DiscussionThis study is the first to investigate PC levels and activity, as well as the perceptions and opinions of HPs regarding the management of respiratory diseases in Spain.
The participating hospitals showed a high level of activity with some heterogeneity, particularly in terms of respiratory admissions and the use of hospital outpatient medications. Most hospitals treated a wide range of diseases, including asthma, COPD, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, and ILD. Treatment for some diseases was restricted to referral hospitals. HP activity could be influenced by the number of pharmacists working in these hospitals, the uneven implementation of new treatments, and the presence of day hospitals.
The presence of referral pharmacists and specific PC in most hospitals was notable. However, referral activities only took up an average of 40% of the HPs' working day, indicating a shortage of specialist pharmacists, unlike in other areas.13 HPs have been recognised for their importance in the management of respiratory disease, especially within the area of community pharmacy.14–16 However, differences appear at the hospital level. Inpatient care involves ongoing and acute care, leading to interventions for health-related problems in 50% of patients.17 Outpatient consultations tend to focus on severe diseases with complex treatments. The SEFH's approach to PC for these patients is based on the MAPEX project, which aims to provide individualised pharmacotherapeutic targets according to the patient's situation.18 Although there was PC activity in outpatient and inpatient settings in most hospitals, patient stratification was very selective. The SEFH's MAPEX initiative developed a stratification model for respiratory diseases using the Capacity, Motivation, and Opportunity model.19
The field of respiratory diseases requires subspecialisation, but our results suggest that HP activity is limited to certain diseases within this field. This finding is underscored by their unequal participation in committees as well as the weight placed on their assessments. The participation of HPs was higher in diseases such as asthma, pneumonia, or those requiring biologics. Involvement in pharmacotherapy management and participation in committees are opportunities to be further developed in the future. Pharmacists already play a clinical role in the setting of COPD or asthma, but they also a role in emerging areas: SARS-CoV-2, critical care, antimicrobials, or the prevention of respiratory viruses.20–25
The marked interest of resident and consultant HPs in relation to PC in respiratory disease was evidenced by their level of participation in expressing their opinions on the topic. They expressed the need to prioritise prevalent diseases (asthma, COPD), but also others such as cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, IDPD, and certain infections. Half of the respondents considered that the inclusion of HPs was “good,” albeit with room for improvement and, in most cases, a need for prioritisation criteria. These results highlight the limited use of prioritisation criteria and suggest that those used in other diseases are acceptable.26 One of the problems identified by the HPs are time constraints due to the need for multitasking. However, there are promising signs of HP specialisation in the area of respiratory disease and its positive impact on clinical outcomes.27,28
Training and the development of competencies are a fundamental aspect of subspecialisation. Our study showed improvements in the 4 areas of HP competencies described in the framework provided by the European Association of Hospital Pharmacists: patient, medicines, system, and practice.29 External or hospital sessions were positively rated by respondents, although provision was limited, there was room for improvement, and certain diseases were identified as priorities. In any case, training should be tailored to meet the specific needs of each hospital in order to optimise PC. Some competencies need improvement, such as the inclusion of HPs in multidisciplinary teams, the use of motivational interviewing, the use of electronic monitoring devices, and telepharmacy.30
This study has limitations. The number of hospitals sampled and pharmacists interviewed was reasonable, but limited. Thus, the results may have been biased by the presence of pharmacists with a greater interest in respiratory diseases. Therefore, although the study provides valuable information, the results may not be representative of all hospitals in Spain. The degree of HP participation in committees or inclusion in sub-areas could also vary for this reason. This limitation is assumed to be minor due to the sufficient number of hospitals analysed. Some Spanish regions are over-represented, but this is aspect is likely to be offset by the participation of hospitals from other regions. Finally, the self-assessment of professional competencies is challenging and should be interpreted within the context of the study.
The study reveals the emerging role of HPs in the PC of respiratory diseases in Spain. This role requires specialisation, inclusion within multidisciplinary teams, and participation in committees. Further work is needed on these issues, given the observed variability between hospitals as well as the margins for improvement. However, specific barriers to this were identified, such as the need for prioritisation criteria, more time for referral activities, and improved training to better address specific healthcare needs and approaches to PC that are best suited to patients.
Contribution to the scientific literatureThis is the first study to explore the level of PC activity, HP inclusion, prioritisation, training, and education in the field of respiratory disease.
The results of this study will help develop pioneering actions tailored to the needs within this field to improve care for patients with respiratory disease.
FundingNone declared.
CRediT authorship contribution statementNoé Garin: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Borja Zarate-Tamames: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Sonia Jornet: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. Eva María García: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. María del Mar López-Gil: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. Gregorio Romero: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. Elena Villamañan: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. Marta Calvin-Lamas: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization.
We would like to thank all the members of the respiratory diseases working group, PNEUMO, for their work.
- Elena Villamañan, Pharmacy Department, Hospital Universitario de la Paz, Madrid, Spain.
- Marta Calvin-Lamas, Pharmacy Department, Complexo Hospitalario Universitario A Coruña, A Coruña, Spain.
- Javier Milara, Pharmacy Department, Consorci Hospital General Universitari de Valencia, Spain.
- Sara Garcia Gil, Pharmacy Department, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Canarias, La Laguna, Spain.
- Hilario Martinez, Pharmacy Department, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, Madrid, Spain.
- Germán Blanco, Pharmacy Department, Hospital Universitario del Henares, Coslada, Spain.
- José Javier Martínez, Pharmacy Department, Hospital Universitario Fundación Alcorcón, Alcorcón, Spain.
- Daniel Echeverría-Esnal, Pharmacy Department, Parc de Salut Mar, Barcelona, Spain.
- Astrid Crespo-Lessmann, Pulmonology Department, Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, Barcelona, Spain.