Skin burns are associated with the presence of metallic components in transdermal drug delivery systems during Magnetic Resonance Imaging, cardioversion, or defibrillation procedures.
The aim of the study was to review the presence of metallic components in marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems in Spain.
MethodFor each pharmaceutical form, the summary of product characteristics was reviewed. If the information was not provided, manufacturers were contacted.
ResultsWe identified 59 marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems of 12 different active substances.
59.3% of patches contained metallic components or their presence could not be ruled out. Information regarding the need to remove the patch was only included in 8 summaries of product characteristics (13.6%)
A table was elaborated and included the following aspects: product, active substance, manufacturer, need to remove the patch before the exposure to magnetic or electric fields, and references.
ConclusionMore than a half of the patches at the time of the study contained metals or their absence could not be confirmed by the manufacturer. However, this information was only included in 13.6% of summaries of product characteristics.
La presencia de partículas metálicas en los parches transdérmicos de medicamentos se ha asociado con riesgo de quemaduras en la piel cuando los pacientes son sometidos a una resonancia magnética, cardioversión eléctrica o desfibrilación.
Por este motivo, el objetivo del trabajo fue analizar la presencia de partículas metálicas en los parches transdérmicos de medicamentos comercializados en España.
MétodoDe cada presentación comercial, se revisó la ficha técnica para comprobar la presencia de estas partículas en su composición. Si no constaba, entonces se contactó con el laboratorio fabricante.
ResultadosSe identificaron 59 presentaciones comerciales de 12 principios activos diferentes. Un 59,3% contenía partículas metálicas o la presencia de las mismas no se pudo descartar. Únicamente, en 8 fichas técnicas (13,6%) constaba la advertencia de retirar el parche cuando el paciente es sometido a alguno de estos procedimientos.
Se elaboró una tabla que incluyó los siguientes aspectos: principio activo, presentación comercial, laboratorio fabricante, necesidad de retirar el parche cuando el paciente es sometido a la exposición de un campo magnético o eléctrico y referencias.
ConclusiónMás de la mitad de los parches comercializados contenían compuestos metálicos o su presencia no pudo descartarse por el laboratorio fabricante. Sin embargo, esta información sólo constaba en un 13,6% de las fichas técnicas.
In 2009, the FDA warned about possible skin burns due to transdermal drug delivery systems with metallic components that are maintained during Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), cardioversion, or defibrillation procedures.1 In this sense, 2 adverse events were reported in which patients who were wearing a nicotine transdermal patch during an MRI experienced burns.2
Transdermal drug delivery systems with metallic components can be electrically conductive. Some patches are formulated with an aluminized backing that could potentially cause injury to the patient if worn during these procedures. MRI systems require the use of radiofrequency (RF) pulses to create the magnetic resonance signal. When conducting materials (i.e., aluminized backing) are placed within the RF field, the result may be a concentration of electrical currents sufficient to cause excessive heating and tissue damage.3,4
Despite the importance of this issue, information regarding the presence of conductive materials in the packaging of transdermal patches is usually lacking.
For this reason, the aim of the study was to review the presence of metallic components in marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems.
MethodsIn December 2022, marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems were identified using the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices database (https://cima.aemps.es/cima/publico/home.html).
For each product, 2 clinical pharmacists from a tertiary hospital reviewed the summary of product characteristics (SmPC) to confirm the need to remove the patch during MRI or other procedures. This information is usually specified as “the patch should be removed before the exposure to magnetic or electric fields” in section “4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use”. If this information was not given, the next step was to check section “6.1 List of excipients” to confirm the presence of metallic components. If they were not specified or they were only present in the liner, manufacturers were contacted by email. They were asked to confirm the presence of metals that could cause skin burns during MRI or other procedures. If no response was received after 1 month, a second follow-up was sent. If no response, the information was registered as “No reply from the manufacturer”.
This research did not include human participants and did not require ethical approval.
ResultsWe identified 59 marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems of 12 different active substances.
Information regarding the need to remove the patch before an MRI or other procedures was only included in 8 SmPCs (13.6%).
59.3% of patches contained metallic components or their absence could not be confirmed by the manufacturer (33.9% and 25.4%, respectively) (Table 1).
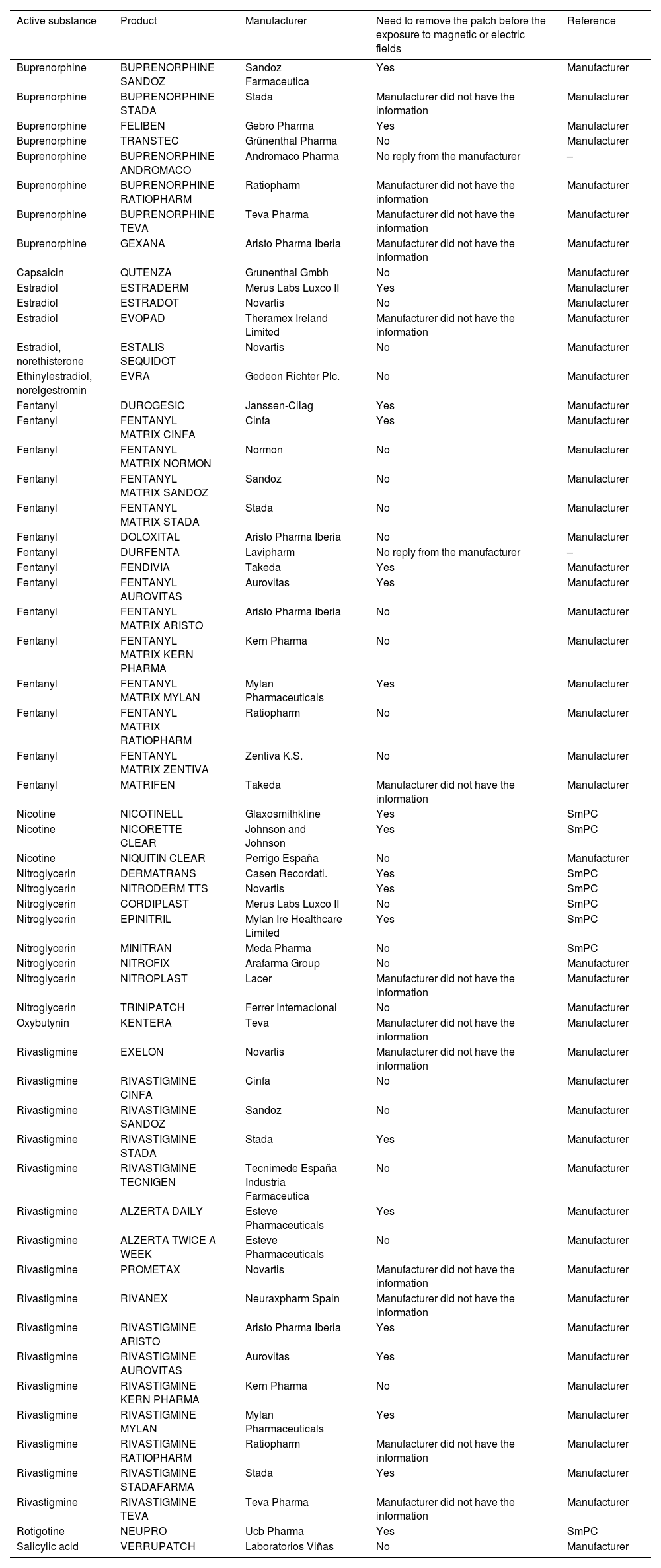
Recommendations regarding the use of transdermal drug delivery systems before the exposure to magnetic or electric fields.
| Active substance | Product | Manufacturer | Need to remove the patch before the exposure to magnetic or electric fields | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buprenorphine | BUPRENORPHINE SANDOZ | Sandoz Farmaceutica | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Buprenorphine | BUPRENORPHINE STADA | Stada | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Buprenorphine | FELIBEN | Gebro Pharma | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Buprenorphine | TRANSTEC | Grünenthal Pharma | No | Manufacturer |
| Buprenorphine | BUPRENORPHINE ANDROMACO | Andromaco Pharma | No reply from the manufacturer | – |
| Buprenorphine | BUPRENORPHINE RATIOPHARM | Ratiopharm | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Buprenorphine | BUPRENORPHINE TEVA | Teva Pharma | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Buprenorphine | GEXANA | Aristo Pharma Iberia | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Capsaicin | QUTENZA | Grunenthal Gmbh | No | Manufacturer |
| Estradiol | ESTRADERM | Merus Labs Luxco II | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Estradiol | ESTRADOT | Novartis | No | Manufacturer |
| Estradiol | EVOPAD | Theramex Ireland Limited | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Estradiol, norethisterone | ESTALIS SEQUIDOT | Novartis | No | Manufacturer |
| Ethinylestradiol, norelgestromin | EVRA | Gedeon Richter Plc. | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | DUROGESIC | Janssen-Cilag | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX CINFA | Cinfa | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX NORMON | Normon | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX SANDOZ | Sandoz | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX STADA | Stada | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | DOLOXITAL | Aristo Pharma Iberia | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | DURFENTA | Lavipharm | No reply from the manufacturer | – |
| Fentanyl | FENDIVIA | Takeda | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL AUROVITAS | Aurovitas | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX ARISTO | Aristo Pharma Iberia | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX KERN PHARMA | Kern Pharma | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX MYLAN | Mylan Pharmaceuticals | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX RATIOPHARM | Ratiopharm | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | FENTANYL MATRIX ZENTIVA | Zentiva K.S. | No | Manufacturer |
| Fentanyl | MATRIFEN | Takeda | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Nicotine | NICOTINELL | Glaxosmithkline | Yes | SmPC |
| Nicotine | NICORETTE CLEAR | Johnson and Johnson | Yes | SmPC |
| Nicotine | NIQUITIN CLEAR | Perrigo España | No | Manufacturer |
| Nitroglycerin | DERMATRANS | Casen Recordati. | Yes | SmPC |
| Nitroglycerin | NITRODERM TTS | Novartis | Yes | SmPC |
| Nitroglycerin | CORDIPLAST | Merus Labs Luxco II | No | SmPC |
| Nitroglycerin | EPINITRIL | Mylan Ire Healthcare Limited | Yes | SmPC |
| Nitroglycerin | MINITRAN | Meda Pharma | No | SmPC |
| Nitroglycerin | NITROFIX | Arafarma Group | No | Manufacturer |
| Nitroglycerin | NITROPLAST | Lacer | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Nitroglycerin | TRINIPATCH | Ferrer Internacional | No | Manufacturer |
| Oxybutynin | KENTERA | Teva | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | EXELON | Novartis | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE CINFA | Cinfa | No | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE SANDOZ | Sandoz | No | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE STADA | Stada | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE TECNIGEN | Tecnimede España Industria Farmaceutica | No | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | ALZERTA DAILY | Esteve Pharmaceuticals | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | ALZERTA TWICE A WEEK | Esteve Pharmaceuticals | No | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | PROMETAX | Novartis | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVANEX | Neuraxpharm Spain | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE ARISTO | Aristo Pharma Iberia | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE AUROVITAS | Aurovitas | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE KERN PHARMA | Kern Pharma | No | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE MYLAN | Mylan Pharmaceuticals | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE RATIOPHARM | Ratiopharm | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE STADAFARMA | Stada | Yes | Manufacturer |
| Rivastigmine | RIVASTIGMINE TEVA | Teva Pharma | Manufacturer did not have the information | Manufacturer |
| Rotigotine | NEUPRO | Ucb Pharma | Yes | SmPC |
| Salicylic acid | VERRUPATCH | Laboratorios Viñas | No | Manufacturer |
SmPC: Summary of Product Characteristics.
A table was elaborated and included the following aspects: active substance, product, manufacturer, need to remove the patch before the exposure to magnetic or electric fields, and references (Table 1).
DiscussionTo our knowledge, this is the first study that analyzes the presence of metallic components in marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems. Some authors have alerted about the risk of serious skin burns associated with the use of patches but none of them have carried out a comprehensive review of their composition.3,4
Several safety issues have been notified with the use of transdermal drug delivery systems, such as errors in the frequency of application or overdosing after cutting the patch.5,6 The need to remove transdermal patches with metallic content before some procedures to prevent skin burns is not well known and could put patients at risk. It is of paramount importance that patients and healthcare professionals be aware of this precaution. In this sense, Radiology, Cardiology, and Emergency Departments should develop safety recommendations regarding the use of patches for patients receiving an MRI, cardioversion, or defibrillation procedures. In our institution, protocols were updated with the information obtained from this review. Currently, patients are questioned about the use of any transdermal patch and, unless it is certain that the patch does not contain metal, patients are counseled to remove it temporarily to avoid unnecessary burns. We believe that the data we compiled can be useful in other healthcare environments to prevent patient harm.
Surprisingly, only 13.6% of available SmPCs included the precaution to remove the patch before an MRI. However, in more than half of the pharmaceutical forms, metallic components were present or could not be excluded. We believe that this cautionary information should be compulsorily included in SmPCs whenever a new patch is authorized by a regulatory agency. The document published by the EMA “A Guideline on Summary of Product Characteristics” establishes that the content of section “4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use” of SmPC should include any information regarding a specific risk when this risk leads to a precaution for use or when healthcare professionals have to be warned of this risk, in our case, skin burns when the patient undergoes an MRI or other procedures.7 Moreover, in section 6.1, all ingredients of the patch (including the adhesive, release liner, and backing film) should be mentioned. However, we found several cases (i.e., Buprenorphine SANDOZ) in which the SmPC did not mention any aluminized component but the manufacturer confirmed its presence.
The main limitation of this study is that the review was performed for transdermal drug delivery systems that were marketed at the time of the study.
ConclusionsMore than a half of the patches at the time of the study contained metals or their absence could not be confirmed by the manufacturer. However, this information was only included in 13.6% of SmPC.
Contribution to scientific literature- Skin burns are associated with the presence of metallic components in transdermal drug delivery systems during Magnetic Resonance Imaging, cardioversion, or defibrillation procedures.
- To our knowledge, this is the first study that analyzes the presence of metals in marketed products of transdermal drug delivery systems.
- Information regarding the need to remove the patch before an MRI or other procedures was only included in 13.6% of the summaries of product characteristics.
- We believe that this comprehensive review could be useful to every healthcare environment to prevent harm when a patient needs to undergo any of these procedures.
Declaration of authorship- Ana de Lorenzo-Pinto: conception and design of the work, data collection, analysis and interpretation of the data, writing of the article and approval of the final version for publication.
- Carmen Redondo-Galán: data collection, analysis and interpretation of the data, writing of the article and approval of the final version for publication.
- Xandra García-González: data collection, critical revision with important intellectual contributions, writing of the article and approval of the final version for publication.
- Carmen Fernández-Álvarez: critical revision with important intellectual contributions and approval of the final version for publication.
- Juan Andueza-Lillo: critical review with important intellectual contributions and approval of the final version for publication.
- María Sanjurjo-Sáez: critical revision with important intellectual contributions and approval of the final version for publication.
FundingNone.
Ethical considerationsNone.
CRediT authorship contribution statementAna de Lorenzo-Pinto: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Carmen Redondo-Galán: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. Xandra García-González: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. Carmen Fernández-Álvarez: Investigation, Supervision, Validation. Juan Andueza-Lillo: Supervision, Validation. María Sanjurjo-Sáez: Supervision, Validation.
None.