As more genes are incorporated into pharmacogenomic care processes and more importance is given to rare variants, the use of targeted capture sequencing panels has been proposed as a very efficient alternative due to their affordability, high throughput, and deep coverage, all of them characteristics of high-quality next-generation sequencing data. The purpose of this study is to describe the prevalence of clinically actionable pharmacogenetic variants previously described in the scientific literature, as well as that of new variants identified by next-generation sequencing technologies, and to evaluate the drugs potentially affected by such variants.
MethodA panel of 18 clinically actionable pharmacogenomics-related genes was evaluated in 41 subjects diagnosed with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant treatment. The prevalence of previously described clinically actionable variants as well as of phenotypes classified according to current interpretation standards was studied. The pharmacological treatments potentially affected by the identified variants were also evaluated. An estimation was made of the prevalence of not previously described, possibly deleterious, variants selected using bioinformatics criteria.
ResultsAll subjects carried clinically actionable variants, with a mean of 4.02 genes affected by each variant per individual. VKORC1, CYP4F2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP2B6 were the most polymorphic genes and were present with actionable phenotypes in more than 50% of patients; 15-50% had actionable phonotypes in UGT1A1, SLCOIBI, CYP2C9 and TPMT and 2-15% in HLA-B, CYP3A5, HLA-A and DPYD. No actionable variants were identified in RYR1, CACNA1S, G6PD, F5 and NUDT15. These variants had the potential to affect response to 84% of the drugs described in the leading pharmacogenetic guidelines. Possibly deleterious variants not previously described accounted for 11.4% of all clinically actionable variants and were present in 12.2% of patients.
ConclusionsThe results obtained show a high prevalence of clinically actionable variants, both common, i.e., previously described in the literature, and rare, i.e., not previously studied with conventional technological approaches. The latter are candidates for a more exhaustive molecular and/or clinical characterization.
A medida que se incorporan más genes a los procesos farmacogenómicos asistenciales y se otorga más importancia a las variantes raras, el uso de paneles de secuenciación dirigida por captura se ha propuesto como una alternativa muy eficiente atendiendo a sus costes, su rendimiento y la cobertura profunda, característica de los datos de secuenciación de nueva generación de alta calidad. El objeto de este trabajo es describir la prevalencia de variantes farmacogenéticas clínicamente procesables descritas previamente en la literatura científica, así como de nuevas variantes identificadas mediante tecnologías de secuenciación de nueva generación y evaluar los fármacos potencialmente afectados por estas variantes.
MétodoSe evaluó un panel de 18 genes relacionados con la farmacogenómica clínicamente procesables en 41 individuos con diagnóstico de cáncer de mama que van a recibir tratamiento adyuvante y neoadyuvante. Se estudió la prevalência de variantes clínicamente procesables previamente descritas en la literatura científica, así como de los fenotipos farmacogenéticos clasificados según los estándares de interpretación actuales. Asimismo, se evaluaron los tratamientos farmacológicos potencialmente afectados por las variantes identificadas. Se estimó la prevalencia de variantes posiblemente deletéreas no descritas previamente seleccionadas con criterios bioinformáticos.
ResultadosTodos los individuos fueron portadores de variantes clínicamente procesables, con una media de 4,02 genes afectados por alguna variante por individuo. Los genes VKORC1, CYP4F2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 y CYP2B6 fueron los más polimórficos, con más de un 50% de pacientes con fenotipos procesables; un 15-50% en UGT1A1, SLCOIBI, CYP2C9 y TPMT y un 2-15% HLA-B, CYP3A5, HLA-A y DPYD. No se identificaron variantes procesables en RYR1, CACNA1S, G6PD, F5 y NUDT15. Estas variantes afectarían a la respuesta de un 84% de los fármacos descritos en las principales guías de farmacogenética. Las variantes posiblemente deletéreas no descritas previamente supusieron un 11,4% del total de variantes clínicamente procesables y están presentes en un 12,2% de los pacientes.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos constatan una alta prevalencia de variantes clínicamente procesables tanto comunes, previamente descritas en la literatura, como raras, no estudiadas con abordajes tecnológicos convencionales y candidatas a una caracterización molecular y/o clínica más exhaustiva.
Pharmacogenetic research has, since its initial stages, identified numerous genes related to the metabolism and transport of, and the response to, drugs showing that many of the genomic variables in these genes are associated with inter-individual pharmacological response variations. Multiple clinical guidelines and other sources of information have been published in the last few years that have helped identify a number of key genes that contain clinically actionable variants, with patients carrying such variants requiring dose adjustments or specific therapeutic strategies1. These gene-drug pairs include metabolizing enzymes (CYP2C19 and clopidogrel2) and transporting (SLCO1B1 and simvastatin3) and other proteins involved in the pharmacological response (RYR1 and halogenated anesthetics)4.
Although pharmacogenetic studies are becoming increasingly popular in clinical centers, most of the genomic variations analyzed are common (i.e. with an allele frequency > 1%)1,5. In fact, most of the currently available high-throughput pharmacogenomic platforms are focused mainly on common variations6. However, several studies based on next generation sequencing (NGS) have confirmed the existence of rare deleterious variants (i.e., with an allele frequency < 1%), which are very frequently found in drug metabolizing enzymes and in the genes coding for pharmacological target proteins. It has been estimated that up to 17% of individuals harbor this kind of variant6,7. Moreover, rare variants have been directly associated with more severe drug response variations than common variants6, as well as with unusual adverse reactions8. For that reason, it is a priority to endow clinical processes with technologies able to identify and manage information not only on the widely studied common variants but particularly on the less known rare variants.
NGS techniques are becoming increasingly popular for the performance of routine genetic studies. Indeed, their cost has been going down in the last few years, the equipment needed is available in a growing number of centers, and there is a rising awareness that rare variants play an important role in the development of disease and in the patients’ response to their medication6. Most pharmacogenomic studies based on NGS techniques correspond to whole exome and whole genome sequencing projects led by large research consortia9,10. Whole exome and whole genome sequencing is still associated with high costs and with problems related to the processing and storage of the large amounts of data generated1,6.11,12. The use of targeted high-throughput sequencing panels, capable of capturing and sequencing a small set of genomic targets to high depth has been proposed as an ideal alternative as it represents a middle ground that maximizes throughput while maintaining the deep coverage characteristic of high-quality NGS data1,6,11,12.
The A Coruña University Hospital Complex has developed a previously described and validated NGS-based pharmacogenomic platform13 intended to support clinical practice and research studies. The platform was designed with a view to studying high evidence, clinically actionable genes and pharmacogenetic regions in addition to genomic regions related to clinical research projects currently underway in the hospital. The idea is to improve the effectiveness of the work carried out in the molecular biology laboratory.
The purpose of this study is to use the NGS platform to identify the prevalence of clinically actionable pharmacogenetic variants in a previously studied population and use NGS to study the new variants identified in the genes that contain clinically actionable variants. In addition, an analysis will be made of the drugs included in pharmacogenetic clinical guidelines that may potentially be affected by such variants.
MethodsDesignThis was a descriptive cross-sectional pharmacogenetic variant prevalence study of a population of 41 patients. The sample was selected based on the availability of genomic sequencing data obtained using the NGS platform developed by the A Coruña University Hospital Complex. The studied population corresponded to the total number of patients recruited by the Hospital within the framework of a project geared towards validating pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenetic biomarkers related with the risk of developing neuropathy following administration of taxanes in the context of the neoadjuvant breast cancer therapy.
Genetic studyThe genomic regions of clinical interest were captured using a personalized capture probe library (SureSelect Target Enrichment Kit for the Illumina paired-end multiplex sequencing method; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, California, USA) and sequenced on the HiSeq 1500 platform (Illumina, San Diego, California) following Illumina protocols14,15. The read depth (number of times a base was sequenced by independent reads) of every nucleotide of genes from the defined genomic regions of interest was >30× (mean: 250×-400×). Analytical validation of this platform has been previously described13. The capture probe library allows sequencing of a total of 433,000 bases. The genes and regions of interest evaluated in this study correspond to a subset of all the genomic regions included in the capture probe library.
Selection of candidate genomic regions of interestA group of genomic regions was selected from 18 pharmacogenomics-related genes that were considered clinically actionable (CACNA1S, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A5, CYP4F2, DPYD, F5, G6PD, HLA-A, HLA-B, NUDT15, RYR1, SLCO1B1, TPMT, UGT1A1 and VKORC1). These genes have been described in several clinical guidelines, including CPIC (Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium)16, DPWG (Dutch Pharmacogenomics Working Group)17 and CPNDS (Canadian Pharmacogenomics Network for Drug Safety)18. A mixed research strategy was developed, which consisted of: a) the development of a specific allele-variant database that allowed an automatic evaluation of the genetic variants and the pharmacogenetic alleles described in the literature; this database comprised 1,027 variants and was developed based on the PharmVar19 and PharmGKB20 databases, and on the GeT-RM pharmacogenomic projects21–23; b) an analysis of the candidate functional variants in the coding regions of genes CACNA1S, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, DPYD, NUDT15, RYR1, SLCO1B1, TPMT, UGT1A1 and VKORC1.
Bioinformatic analysisThe sequence analysis was carried out using a purpose-developed bioinformatic algorithm that included the demultiplexing of the samples as well as all the steps needed to obtain a validated report of the annotated variants, together with their coverage and quality parameters13. Haplotypes were assigned following a purpose-designed algorithm that used variant-allele translation tables developed together with the variant files (vcf format) and the coverage data (cov format) obtained from each sample13.
The analysis of the copy number variants (CNVs) and the structural variants of CYP2D6 was carried out using a previously-described and validated comparative coverage depth strategy13,24.
Genotype interpretationIt was done using the genotype-to-phenotype prediction classification system described in pharmacogenomic prescription guidelines and recommendations. These standards are summarized below. Phenotypes were determined by genotyping sets (haplotypes) of genetic variants known as star alleles “*”. Every patient has two star alleles that are collectively referred to as a diplotype or genotype (e.g., *1/*2). Each star allele was then assigned a function (i.e., no, decreased, normal or increased function) and a corresponding numerical activity level based on the evidence available on databases and in leading publications such as PharmVar. The activity levels of the two alleles in each individual were combined and translated into a phenotype (poor, intermediate, normal, rapid, ultrarapid) that was then linked to a selection of specific drugs and a dosing recommendation22,25.
Clinical actionabilityIt was determined based on the prescription recommendations described in the CPIC, DPWG and CPNDS clinical guidelines16–18. Three different categories were established: “non actionable”, “conditional” and “actionable”. Table 2 in the Annex includes a detailed description of this classification.
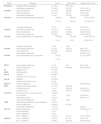
Genotypes identified and their frequency in the studied population, grouped by gene and phenotype
| Gene | Phenotype | Genotype | Nr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CACNA1S | Negative | No high-risk MH variant present (rs1800559, rs772226819) | 41 (100) |
| 4l (l00) | |||
| *14/*6a | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1A/*6A; *4A/*9A | 7 (17.1) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | *1A/*7A; *5A/*6A | 1 (2.4) | |
| *4A/*9A; *1A/*6A | 4 (9,8) | ||
| *5A/*6A; *1A/*7A | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *6A/*6a | 1 (2.4) | ||
| CYP2B6 | *1A/*r | 14 (34.1) | |
| Normal metabolizer | *1A/*2a | 3 (7.3) | |
| *1A/*5a | 3 (7.3) | ||
| *5A/*5a | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1A/*4a | 2 (4.9) | ||
| Rapid metabolizer | *22A/*5a | 1 (2.4) | |
| *2A/*4a | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *4A/*5a | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *17/*2a | 1 (2.4) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | *1A/*2a | 9 (22) | |
| CYP2C19 | *1A/*2B | 4 (9,8) | |
| Normal metabolizer | *1A/*r | 18 (43.9) | |
| Rapid metabolizer | *1A/*17 | 6 (14.6) | |
| Ultrarapid metabolizer | *17/*17 | 3 (7.3) | |
| CYP2C9 | Intermediate metabolizer | *1/*2 | 7 (17.1) 6 (14.6) |
| Normal metabolizer | *1/*3 | 28 (68.3) | |
| *10A/*5 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1A/*3A | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1A/*4A | 6 (14.6) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | *1A/*5 | 2 (4.9) | |
| *2A/*4A | 7 (17.1) | ||
| *2A/*5 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *4A/*41 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| CYP2D6 | *1A/*1A | 5 (12.2) | |
| *1A/*2A | 9 (22) | ||
| Normal metabolizer | *1A/*41 | 2 (4.9) | |
| *2A/*41 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *2A/*9 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *2Ax2/*4A | 2 (4.9) | ||
| Poor metabolizer | *6A/*5 | 1 (2.4) | |
| Ultrarapid metabolizer | *1Ax2/*1A | 1 (2.4) | |
| Intermediate metabolizer | *1A/*3C | 5 (12.2) | |
| CYP3A5 | Poor metabolizer | *3C/*3C | 35 (85.4) |
| *3C/*6 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1/*3 | 10 (24.4) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | *2/*3 | 11 (26.8) | |
| CYP4F2 | *3/*3 | 1 (2.4) | |
| Normal metabolizer | 16 (39) | ||
| Poor metabolizer | *2+3/*2+3 *2+3/*3 | 2 (4.9) 1 (2.4) | |
| DPYD | Intermediate metabolizer | *1/c.1905+1G>A (*2A) | 1 (2.4) |
| Normal metabolizer | 40 (97.6) | ||
| F5 | Negative | Non-carrier FVL | 41 (100) |
| G6PD | Normal activity | B (homozygosis) B (homozygosis) | 1 (2.4) 40 (97.6) |
| HLA-A | Negative | c.*66A= (rs1061235-A)/c.*66A= (rs1061235-A) | 38 (92.7) |
| Positive (HLA-A*31:01 het.) | c.*66A= (rs1061235-A)/c.*66A>T (rs1061235-T) (*31:01) | 3 (7.3) | |
| B*07:02:01/B*35:08:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*07:02:01/B*37:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*07:02:01/B*38:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*08:01:01/B*14:02:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*08:01:01/B*15:01:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*08:01:01/B*18:01:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*08:01:01/B*35:08:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*08:01:01/B*44:02:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| HLA-B | Negative | B*13:02:01/B*14:02:01 | 1 (2.4) |
| B*15:01:01:01/B*49:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*15:16:01/B*44:03:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*18:01:01:01/B*53:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*35:01:01:01/B*14:02:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*35:01:01:01/B*18:01:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*40:02:01/B*14:02:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*40:02:01/B*55:01:01 | 2 (4.9) | ||
| B*40:04/B*14:02:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*41:01/B*44:03:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:02:01:01/B*15:16:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:02:01:01/B*18:01:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:02:01:01/B*27:02:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:02:01:01/B*51:01:07 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:03:01/B*44:02:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:03:01/B*49:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*44:03:01/B*51:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| Negative |
|
| |
| HLA-B | B*49:01:01/B*55:01:01 | 2 (4.9) | |
| B*50:01:01/B*51:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*51:01:01/B*35:01:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*51:01:01/B*40:02:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*51:01:01/B*44:02:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*51:01:01/B*50:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*53:01:01/B*38:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*55:01:01/B*15:16:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*13:02:01/B*58:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| Positive (HLA-B*58:01 het.) | B*37:01:01/B*58:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | |
| B*44:02:01:01/B*58:01:01 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| B*58:01:01/B*27:05:02 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| NUDT15 | Normal metabolizer | *1A/*1A | 41 (100) |
| RYR1 | Negative | No high-risk MH variant present | 41 (100) |
| Increased function | *14/*1B | 1 (2.4) | |
| *1A/*1A | 2 (4.9) | ||
| Normal function | *1A/*1B | 11 (26.8) | |
| *1A/*21 | 3 (7.3) | ||
| *1B/*21 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| Normal function; increased function | *1A/*14; *1B/*4 | 1 (2.4) | |
| *1B/*4; *1A/*14 | 8 (19,5) | ||
| Poor function | *15/*5 | 1 (2.4) | |
| SLCO1B1 | *14/*15 | 2 (4.9) | |
| *14/*17 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *14/*5; *15/*4 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *15/*1B | 1 (2.4) | ||
| Decreased function | *15/*4; *14/*5 | 1 (2.4) | |
| *1A/*15; *1B/*5 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1A/*17; *21/*5 | 1 (2.4) | ||
| *1A/*5 | 3 (7.3) | ||
| *1B/*5; *1A/*15 | 2 (4.9) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | *1/*2 | 2 (4.9) | |
| TPMT | Intermediate metabolizer; | *1/*3A; *3B/*3C | 3 (7.3) |
| Poor metabolizer | *3B/*3C; *1/*3A | 34 (82.9) | |
| Normal metabolizer | *1/*1 | 2 (4.9) | |
| *1/*28+60; *28/*60 | 2 (4.9) | ||
| *1/*28+60+93;*28+60/*93 | 4 (9,8) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | *28/*60; *1/*28+60 | 1 (2.4) | |
| *28+60/*93; *1/*28+60+93 | 5 (12.2) | ||
| UGT1A1 | *28+60+93/*60 | 5 (12.2) | |
| Normal metabolizer | *1/*1 | 13 (31.7) | |
| *1/*60 | 8 (19,5) | ||
| Poor metabolizer | *28+60+93/*28+60+93 | 1 (2.4) | |
| Rapid metabolizer | *1/*36+60; *36/*60 | 1 (2.4) | |
| VKORC1 | Normal sensitivity to coumarins | Non-carrier c.-1639G>A (rs9923231) | 13 (31.7) |
| Highly increased sensitivity to coumarins | Homozygous carrier c.-1639G>A (rs9923231) | 5 (12.2) | |
| Increased sensitivity to coumarins | Heterozygous carrier c.-1639G>A (rs9923231) | 23 (56.1) |
FVL: factor V Leiden; het.: heterozygosis; hom.: homozygosis; MH: malignant hyperthermia.
The B allele in the G6PD gene corresponded to the wild-type reference allele.
In the first place, a clinically actionable allele prevalence study was conducted; alleles were grouped by patient and by gene. Secondly, an analysis was carried out of the prevalence of the different pharmacogenetic phenotypes obtained from the genotype interpretation process. Thirdly, the clinical actionability of the pharmacogenetic phenotypes identified foe each of the drugs described in pharmacogenetic clinical guidelines was established. Lastly, a bioinformatic algorithm was used to select the potentially deleterious candidate variables using the following filtering criteria: they had to be rare variants (whose gnomAD population frequency was below 1%) located in coding regions (gene coding exons), which could bring about changes in the protein sequence (nonsense, missense) and with a phred score above 20 for the CADD bioinformatic predictor (the phred score is used to select the most deleterious 1% of all possible variants of the gene).
Ethical-legal aspectsThe present study was approved by the Drug Research Ethics Committee of Galicia (CEIm-G ID 2017/437). All the patients included gave their informed consent to participate in the study.
ResultsThe patient sample was made up of a total of 41 individuals of whom 40 were female (97.6%). Mean age was 57.05 ± 11.23 years (range 36-77 years).
The sequencing and bioinformatic analysis process of the 41 analyzed patients resulted in the identification of 6,802 variants in the genes for whose coding regions there was sequencing data available. A total of 2,216 of these variants were found in the coding genes that had been coded in full. Removing duplications, a total of 175 unique variants were identified. Table 3 in the Annex includes a list of the genetic variants identified in this population.
Genetic variants identified, frequency in the study population and other associated data
| GENE | PROTEIN_NAME | CDNA_NAME | CHROMOSOMIC_NAME | GENE_ZONE | PROTO_TYPE | SPLICING_REGION | IN_DATASET | CADD_PHREDD | EXAC_FREQ | GNOMAD_FREQ | DBSNP_FREQ | NUMBER_HETEROZYGOTES | HETEROZYGOTES_FREQ | NUMBER_HOMOZYGOTES | HOMOZYGOTES_FREQ | ALLELE_FREQ |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.(Leu238=) | NM_000767.4:c.714G>A | NC_000019.9:g.41515192G>A | Cod ng exon | Synonymoys | NO | NO | 0,031 | 0,0891 | 0,3094 | 0,0891 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.(Pro72=) | NM_000767.4:c.216G>C | NC_000019.9:g.41509950G>C | Cod ng exon | Synonymoys | NO | NO | 3,718 | 5,043 | 4,9602 | 5,0489 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Arg140Gln | NM_000767.4:c.419G>A | NC_000019.9:g.41510286G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 20,9 | 0,3455 | 0,3428 | 0,3357 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Arg22Cys | NM_000767.4:c.64C>T | NC_000019.9:g.41497274C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 17,44 | 4,896 | 4,8301 | 4,8903 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Arg487Cys | NM_000767.4:c.1459C>T | NC_000019.9:g.41522715C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 0,31 | 9,0906 | 8,7843 | 8,9391 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Gln172His | NM_000767.4:c.516G>T | NC_000019.9:g.41512841G>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 0,001 | 27,319 | 27,0857 | 27,4879 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Gln21Leu | NM_000767.4:c.62A>T | NC_000019.9:g.41497272A>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | NO | 0,117 | 0,3857 | 0,4042 | 0,3846 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Lys262Arg | NM_000767.4:c.785A>G | NC_000019.9:g.41515263A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 0,001 | 5,6317 | 14,7183 | 5,6317 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| CYP2B6 | NP_000758.1:p.Lys61Thr | NM_000767.4:c.182A>C | NC_000019.9:g.41509916A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | YES | NO | 15,67 | 0,0017 | 0,0032 | 0,0017 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 18,29268293 |
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.1153-9C>T | NC_000019.9:g.41518570C>T | Intron | YES | NO | 1,345 | 0,019 | 0,0163 | 0,019 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 18,29268293 | ||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.1294+53C>T | NC_000019.9:g.41518773C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 1,133 | 26,6997 | 31,6893 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.334+34T>G | NC_000019.9:g.41510102T>G | Intron | NO | NO | 11,39 | 0,0009 | 0,3152 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 32,31707317 | |||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.335-14C>G | NC_000019.9:g.41510188C>G | Intron | NO | NO | 6,01 | 0,2709 | 0,2791 | 0,2641 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.485-1007C>G | NC_000019.9:g.41511803C>G | Intron | NO | NO | 9,023 | 28,318 | 29,1334 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.485-18C>T | NC_000019.9:g.41512792C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 4,528 | 33,5284 | 33,1657 | 33,3375 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 32,31707317 | ||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.646-17C>T | NC_000019.9:g.41515107C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 4,245 | 1,8462 | 1,7689 | 2,0419 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.822+183G>A | NC_000019.9:g.41515483G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 2,561 | 68,8008 | 76,1581 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 0 | 8,536585366 | ||||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.822+40A>T | NC_000019.9:g.41515340A>T | Intron | NO | NO | 2,446 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.822+50G>A | NC_000019.9:g.41515350G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 5,156 | 1,3805 | 0,2056 | 1,3805 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.823-197T>C | NC_000019.9:g.41515702T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 1,759 | 66,5122 | 73,4824 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | ||||
| CYP2B6 | NM_000767.4:c.-82T>C | NC_000019.9:g.41497129T>C | Intron | NO | YES | 1,6546 | 1,6374 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 0 | 8,536585366 | |||||
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.(Pro227=) | NM_000769.2:c.681G>A | NC_000010.10:g.96541616G>A | Coding exon | Synonymoys | NO | YES | 5,686 | 18,5627 | 17,4893 | 18,7069 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 0 | 8,536585366 | |
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.(Pro33=) | NM_000769.2:c.99T>C | NC_000010.10:g.96522561T>C | Coding exon | Synonymoys | NO | NO | 0,096 | 7,8891 | 7,6424 | 7,9405 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.(Val330=) | NM_000769.2:c.990C>T | NC_000010.10:g.96602622C>T | Coding exon | Synonymoys | NO | NO | 7,62 | 18,3515 | 17,7101 | 18,501 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.Arg125His | NM_000769.2:c.374G>A | NC_000010.10:g.96535189G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | NO | 23 | 0,0297 | 0,0343 | 0,0297 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.Glu92Asp | NM_000769.2:c.276G>C | NC_000010.10:g.96534922G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 0,026 | 2,3597 | 2,2587 | 2,3019 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.Ile222Val | NM_000769.2:c.664A>G | NC_000010.10:g.96541599A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | NO | 0,02 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| CYP2C19 | NP_000760.1:p.Val331Ile | NM_000769.2:c.991G>A | NC_000010.10:g.96602623G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | NO | 0,001 | 6,2417 | 5,9734 | 6,1866 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| CYP2C19 | NM_000769.2:c.332-23A>G | NC_000010.10:g.96535124A>G | Intron | NO | NO | 5,31 | 18,6267 | 17,9538 | 18,7942 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 7,926829268 | ||
| CYP2C19 | NM_000769.2:c.-806C>T | NC_000010.10:g.96521657C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 20,5184 | 15,3155 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | |||||
| CYP2C19 | NM_000769.2:c.820-51C>G | NC_000010.10:g.96580202C>G | Intron | NO | NO | 1,805 | 18,6111 | 17,9388 | 18,7809 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 3,048780488 | ||
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.(Gly475=) | NM_000771.3:c.1425A>T | NC_000010.10:g.96748737A>T | Coding exon | Synonymoys | NO | NO | 0,01 | 6,3769 | 6,1589 | 6,3181 | 29 | 70,73170732 | 0 | 17,68292683 | |
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.(Phe267=) | NM_000771.3:c.801C>T | NC_000010.10:g.96709023C>T | Coding exon | Synonymoys | NO | NO | 15,43 | 0,0812 | 0,0831 | 0,0811 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.Arg144Cys | NM_000771.3:c.430C>T | NC_000010.10:g.96702047C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymoys | NO | YES | 29,1 | 9,1435 | 9,0956 | 8,971 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | |
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.Ile359Leu | NM_000771.3:c.1075A>C | NC_000010.10:g.96741053A>C | Cod ng exor | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 20,4 | 6,3706 | 6,1539 | 6,3104 | 0 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,219512195 | |
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.Pro33Ser | NM_000771.3:c.97C>T | NC_000010.10:g.96698536C>T | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 24,5 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 0 | 17,07317073 | ||||
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.Val153Ala | NM_000771.3:c.458T>C | NC_000010.10:g.96702075T>C | Cod ng exor | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 23,8 | 0,0049 | 0,0056 | 0,0049 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2C9 | NP_000762.2:p.Val5Ala | NM_000771.3:c.14T>C | NC_000010.10:g.96698453T>C | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 13,63 | 0,0305 | 0,0273 | 0,0301 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2C9 | NM_000771.3:c.169-14G>C | NC_000010.10:g.96701601G>C | Intron | NO | NO | 0,859 | 9,4384 | 9,4439 | 9,2589 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| CYP2C9 | NM_000771.3:c.482-2313A>T | NC_000010.10:g.96705223A>T | Intron | NO | NO | 0,482 | 19,4066 | 14,4768 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 0 | 9,756097561 | ||||
| CYP2C9 | NM_000771.3:c.820-6326A>C | NC_000010.10:g.96725535A>C | Intron | NO | NO | 0,336 | 18,5248 | 16,3938 | 0 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| CYP2C9 | NM_000771.3:c.962-32T>C | NC_000010.10:g.96740908T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 8,36 | 4,7688 | 4,5508 | 4,6612 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 23,17073171 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Gly176=) | NM_000106.5:c.528T>C | NC_000022.10:g.42524924A>G | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 0,044 | 28,1514 | 14,5047 | 28,1514 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(His232=) | NM_000106.5:c.696T>C | NC_000022.10:g.42524323A>G | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 0,006 | 0,7238 | 0,6731 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 0 | 11,58536585 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(His361=) | NM_000106.5:c.1083T>C | NC_000022.10:g.42523539A>G | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 2,934 | 1,0587 | 0,6735 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 0 | 11,58536585 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Phe112=) | NM_000106.5:c.336C>T | NC_000022.10:g.42525756G>A | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 4,543 | 7,7657 | 7,7645 | 0 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,219512195 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Phe219=) | NM_000106.5:c.657T>C | NC_000022.10:g.42524795A>G | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | YES | NO | 0,002 | 34,3437 | 28,8157 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Pro267=) | NM_000106.5:c.801C>A | NC_000022.10:g.42524218G>T | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 5,175 | 1,0593 | 0,9592 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Pro325=) | NM_000106.5:c.975G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42523854C>T | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | YES | NO | 12,86 | 0,3337 | 0,2929 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Ser401=) | NM_000106.5:c.1203G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42522965C>T | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 10,41 | 0,3912 | 0,4404 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 0 | 6,097560976 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Thr98=) | NM_000106.5:c.294C>G | NC_000022.10:g.42525798G>C | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 1,268 | 12,3687 | 11,4005 | 87,8645 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 0 | 9,756097561 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Val119=) | NM_000106.5:c.357G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42525183C>T | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | YES | NO | 7,5 | 0,0009 | 0,0033 | 0,0009 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 0 | 9,756097561 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.(Val136=) | NM_000106.5:c.408C>G | NC_000022.10:g.42525132G>C | Cod ng exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 0,421 | 45,1474 | 44,843 | 55,0625 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 23,17073171 |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Ala122Ser | NM_000106.5:c.364G>T | NC_000022.10:g.42525176C>A | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 6,612 | 0,0681 | 0,0724 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 0 | 6,707317073 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Arg259Glyfs*2 | NM_000106.5:c.775deiA | NC_000022.10:g.42524244delT | Cod ng exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 24,2 | 1,3082 | 1,247 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Arg329Leu | NM_000106.5:c.986G>T | NC_000022.10:g.42523636C>A | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | NO | 23,4 | 7,5641 | 2,8174 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 0 | 6,097560976 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Arg365His | NM_000106.5:c.1094G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42523528C>T | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 35 | 12,1059 | 9,3852 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Asn141Ser | NM_000106.5:c.422A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42525118T>C | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 15,79 | 0,0008 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Cys296Arg | NM_000106.5:c.886T>C | NC_000022.10:g.42523943A>G | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,042 | 65,6656 | 65,5519 | 65,6025 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 0 | 10,36585366 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Gln151Glu | NM_000106.5:c.451C>G | NC_000022.10:g.42525089G>C | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 0,002 | 0,2392 | 0,2333 | 99,7663 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Glu216Ala | NM_000106.5:c.647A>C | NC_000022.10:g.42524805T>G | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 12,96 | 0,0039 | 0,0032 | 0,0039 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Gly212Glu | NM_000106.5:c.635G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42524817C>T | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 0,001 | 0,7325 | 0,7045 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 0 | 6,097560976 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Gly373Ser | NM_000106.5:c.1117G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42523505C>T | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 15,94 | 1,7085 | 0,3559 | 80,7692 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 0 | 17,07317073 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.His94Arg | NM_000106.5:c.281A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42525811T>C | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 0,001 | 11,562 | 9,9999 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Leu91Met | NM_000106.5:c.271C>A | NC_000022.10:g.42525821G>T | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 23,1 | 11,3402 | 9,5161 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Lys281del | NM_000106.5:c.841_843delAAG | NC_000022.10:g.42524178_42524180delTCT | Coding exon | Deie ion | YES | YES | 18,02 | 1,8972 | 1,5486 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 36,58536585 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Pro34Ser | NM_000106.5:c.100C>T | NC_00002210:g.42526694G>A | Cod ng exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 24,9 | 24,6687 | 20,6826 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Thr486Ser | NM_000106.5:c.1457C>G | NC_000022.10:g.42522613G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 0,001 | 45,556 | 44,7491 | 54,6687 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Trp152Glyfs*2 | NM_000106.5:c.454delT | NC_000022.10:g.42525086delA | Coding exon | =rame Shift | NO | YES | 23,5 | 0,7929 | 0,8049 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Tyr355Cys | NM_000106.5:c.1064A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42523558T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 22,1 | 0,7697 | 0,2337 | 0,7697 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Val11Met | NM_000106.5:c.31G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42526763C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 5,192 | 5,3012 | 3,9348 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 34,14634146 | |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Val370Ile | NM_000106.5:c.1108G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42523514C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 2,428 | 1,3867 | 0,1439 | 1,3867 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 24,3902439 |
| CYP2D6 | NP_000097.3:p.Val7Met | NM_000106.5:c.19G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42526775C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 2,415 | 0,328 | 0,2351 | 0,3067 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 10,97560976 |
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.*112C>T | NC_000022.10:g.42522464G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 0,5889 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.*184C>T | NC_000022.10:g.42522392G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 18,8933 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.*227A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42522349T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 0,1053 | 0,3395 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | |||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.*264A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42522312T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 71,749 | 76,0982 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.*26C>T | NC_000022.10:g.42522550G>A | UTR | NO | NO | 2,417 | 2,2075 | 1,5757 | 2,2075 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 0 | 17,07317073 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.1173+40C>A | NC_000022.10:g.42523409G>T | Intron | NO | NO | 0,591 | 34,0283 | 33,3998 | 34,0282 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.1174-9T>C | NC_000022.10:g.42523003A>G | Intron | YES | NO | 2,238 | 5,9767 | 37,7906 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.1316-20C>T | NC_00002210:g.42522774G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 0,842 | 0,277 | 0,1163 | 0,277 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.-1589G>C | NC_000022.10:g.42528382C>G | Intron | NO | NO | 79,6524 | 16,254 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 13,41463415 | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.-1775A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42528568T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 72,4672 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 9,756097561 | |||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.180+34C>G | NC_000022.10:g.42526580G>C | Intron | NO | NO | 0,38 | 67,1945 | 66,5612 | 32,6762 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.180+41A>C | NC_000022.10:g.42526573T>G | Intron | NO | NO | 1,108 | 65,6614 | 66,3199 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 9,756097561 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.180+43G>C | NC_000022.10:g.42526571C>G | Intron | NO | NO | 1,754 | 65,3955 | 66,3607 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 17,68292683 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.180+47C>T | NC_000022.10:g.42526567G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 0,227 | 64,926 | 66,3613 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.181-41G>T | NC_000022.10:g.42525952C>A | Intron | NO | NO | 1,647 | 47,3976 | 44,0387 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 26 | 63,41463415 | 39,02439024 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.-2183G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42528976C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 21,9583 | 26,9369 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.-44_-43insG | NC_000022.10:g.4252684142526842insC | UTR | NO | NO | 4,969 | 1,5689 | 1,4032 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.505+32A>G | NC_000022.10:g.42525003T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 5,149 | 0,2129 | 0,1292 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 6,707317073 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.506-1G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42524947C>T | Intron | YES | YES | 23 | 17,0761 | 13,8417 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.506-29G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42524975C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 6,845 | 3,6561 | 1,3377 | 3,6561 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.506-36G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42524982C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 6,256 | 3,6651 | 0,812 | 3,6651 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.666+43C>T | NC_000022.10:g.42524743G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 2,822 | 33,1398 | 29,4826 | 33,1398 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 6,707317073 | ||
| CYP2D6 | NM_000106.5:c.985+39G>A | NC_000022.10:g.42523805C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 6,015 | 8,0816 | 7,8544 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 | |||
| CYP3A5 | NP_000768.1:p.(Lys208=) | NM_000777.4:c.624G>A | NC_000007.13:g.99262835C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 9,935 | 1,1982 | 1,2956 | 1,3273 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 30,48780488 |
| CYP3A5 | NP_000768.1:p.Thr398Asn | NM_000777.4:c.1193C>A | NC_000007.13:g.99250236G>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 0,084 | 0,3535 | 0,3243 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 0 | 6,707317073 | ||
| CYP3A5 | NM_000777.4:c.219-237G>A | NC_000007.13:g.99270539C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 3,375 | 26,3653 | 0 | 41 | 100 | 50 | |||||
| CYP4F2 | NP_001073.3:p.(His343=) | NM_001082.4:c.1029C>T | NC_000019.9:g.15996820G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 3,495 | 28,6405 | 28,2101 | 28,429 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 0 | 6,097560976 | |
| CYP4F2 | NP_001073.3:p.(Pro55=) | NM_001082.4:c.165A>G | NC_000019.9:g.16008257T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 0,007 | 16,8004 | 16,5553 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||
| CYP4F2 | NP_001073.3:p.Gly185Val | NM_001082.4:c.554G>T | NC_000019.9:g.16001215C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 23,2 | 4,7139 | 4,757 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||
| CYP4F2 | NP_001073.3:p.Trp12Gly | NM_001082.4:c.34T>G | NC_000019.9:g.16008388A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 0,001 | 16,0631 | 15,7477 | 39 | 95,12195122 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 26,2195122 | |
| CYP4F2 | NP_001073.3:p.Val433Met | NM_001082.4:c.1297G>A | NC_000019.9:g.15990431C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 26,1 | 27,2576 | 26,6086 | 27,1159 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 29,87804878 |
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.(Phe632=) | NM_000110.3:c.1896T>C | NC_000001.10:g.97915624A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | NO | 0,005 | 4,6849 | 5,043 | 4,7058 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 38 | 92,68292683 | 48,17073171 |
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Arg29Cys | NM_000110.3:c.85C>T | NC_000001.10:g.98348885G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 23,7 | 76,5172 | 76,602 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 0 | 7,317073171 | ||
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Ile543Val | NM_000110.3:c.1627A>G | NC_000001.10:g.97981395T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 9,639 | 19,2959 | 19,5184 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 7,926829268 | |
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Lys259Glu | NM_000110.3:c.775A>G | NC_000001.10:g.98144726T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 23,4 | 1,0218 | 0,608 | 0,9753 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Met166Val | NM_000110.3:c.496A>G | NC_000001.10:g.98165091T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 24,5 | 8,6366 | 8,585 | 8,5182 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 |
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Met406Ile | NM_000110.3:c.1218G>A | NC_000001.10:g.98039437C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 17,28 | 0,6046 | 0,6736 | 0,6646 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 0 | 9,146341463 | |
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Ser534Asn | NM_000110.3:c.1601G>A | NC_000001.10:g.97981421C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 23,4 | 1,4159 | 1,4336 | 34 | 82,92682927 | 0 | 20,73170732 | ||
| DPYD | NP_000101.2:p.Val732Ile | NM_000110.3:c.2194G>A | NC_000001.10:g.97770920C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 25,9 | 4,6473 | 4,5309 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| DPYD | NM_000110.3:c.1129-15T>C | NC_000001.10:g.98039541A>G | Intron | NO | NO | 5,766 | 10,4577 | 9,6922 | 10,2832 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 30,48780488 | ||
| DPYD | NM_000110.3:c.1740+39C>T | NC_000001.10:g.97981243G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 3,247 | 18,9927 | 18,8407 | 18,9222 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | |||
| DPYD | NM_000110.3:c.1740+40A>G | NC_000001.10:g.97981242T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 1,556 | 66,0886 | 63,284 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||||
| DPYD | NM_000110.3:c.1905+1G>A | NC_000001.10:g.97915614C>T | Intron | YES | YES | 23,7 | 0,5229 | 0,5689 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 0 | 10,97560976 | ||||
| DPYD | NM_000110.3:c.2300-39G>A | NC_000001.10:g.97700589C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 6,088 | 11,761 | 11,6491 | 11,6432 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |||
| G6PD | NP_001035810.1:p.(Tyr437=) | NM_001042351.2:c.1311C>T | NC_000023.10:g.153760654G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 6,988 | 16,7207 | 16,356 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-A | NM_001242758.1:c.*66A>T | NC_000006.11:g.29913298A>T | UTR | NO | YES | 10,48 | 4,7044 | 8,5064 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala15=) | NM_005514.7:c.45G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324891C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 15,43 | 11,6352 | 9,1342 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 38 | 92,68292683 | 48,17073171 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala159=) | NM_005514.7:c.477C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324086G>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 6,543 | 44,9056 | 48,8756 | 53,5536 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala16=) | NM_005514.7:c.48C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324888G>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 2,301 | 25,0682 | 30,1801 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala206=) | NM_005514.7:c.618T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323945A>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | YES | 1,19 | 80,3351 | 84,5789 | 26 | 63,41463415 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 24,3902439 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala24=) | NM_005514.7:c.72C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324864G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | YES | 10,39 | 2,3516 | 3,8903 | 40 | 97,56097561 | 0 | 24,3902439 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala5=) | NM_005514.7:c.15G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324921C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 15,82 | 15,204 | 13,4031 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 0 | 5,487804878 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ala95=) | NM_005514.7:c.285A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324523T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 6,396 | 4,0786 | 2,8874 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Arg103=) | NM_005514.7:c.309G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324499C>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 9,174 | 2,5521 | 3,0411 | 97,2402 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 14,02439024 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Arg180=) | NM_005514.7:c.540G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324023C>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 8,168 | 0,0027 | 0,0009 | 0,6043 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 14,63414634 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Arg258=) | NM_005514.7:c.774A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323215T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,052 | 25,0375 | 6,727 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 0 | 5,487804878 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Arg59=) | NM_005514.7:c.175A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324633T>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 9,514 | 0,1033 | 0,2354 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 14,02439024 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Arg68=) | NM_005514.7:c.204A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324604T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 6,274 | 13,0273 | 15,518 | 13,0273 | 23 | 56,09756098 | 0 | 14,02439024 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Asn151=) | NM_005514.7:c.453C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324110G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 10,05 | 4,835 | 2,5737 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 31,70731707 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Asn198=) | NM_005514.7:c.594C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323969G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 7,319 | 1,8941 | 0,9147 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 20,73170732 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Asp153=) | NM_005514.7:c.459C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324104G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 15,07 | 22,1871 | 14,7826 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 34,14634146 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Asp262=) | NM_005514.7:c.786T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323203A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,172 | 7,3409 | 8,1132 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Gln78=) | NM_005514.7:c.234G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324574C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 10,62 | 3,6213 | 2,4897 | 3,5743 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Glu288=) | NM_005514.7:c.864G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323125C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 9,834 | 0,0049 | 0,0044 | 8 | 19,51219512 | 32 | 78,04878049 | 43,90243902 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Glu82=) | NM_005514.7:c.246G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324562C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 12,07 | 10,5664 | 10,2713 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 19,51219512 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Gly231=) | NM_005514.7:c.693T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323296A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 7,193 | 84,891 | 85,0889 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 14,02439024 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Gly245=) | NM_005514.7:c.735C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323254G>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 6,808 | 7,6505 | 0,9069 | 92,4079 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(His137=) | NM_005514.7:c.411T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324152A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,062 | 3,7801 | 3,3778 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(His212=) | NM_005514.7:c.636C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323353G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 1,129 | 39,6858 | 39,8976 | 39 | 95,12195122 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 26,2195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(His287=) | NM_005514.7:c.861T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323128A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,162 | 17,3756 | 4,5488 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 28,65853659 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ile47=) | NM_005514.7:c.141C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324667G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 9,471 | 7,4514 | 5,7783 | 32 | 78,04878049 | 0 | 19,51219512 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Leu102=) | NM_005514.7:c.306G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324502C>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 12,65 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 29,26829268 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Leu119=) | NM_005514.7:c.357C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324206G>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,613 | 92,1658 | 23 | 56,09756098 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 29,87804878 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Leu119=) | NM_005514.7:c.357C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324206G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 2,647 | 7,1791 | 8,6844 | 34 | 82,92682927 | 0 | 20,73170732 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Lys145=) | NM_005514.7:c.435G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324128C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 10,74 | 8,2054 | 6,8021 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 0 | 5,487804878 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Pro129=) | NM_005514.7:c.387G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324176C>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 10,76 | 7,772 | 8,9058 | 92,228 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 34,75609756 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Pro291=) | NM_005514.7:c.873G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323116C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 12,46 | 4,7356 | 3,3684 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Pro300=) | NM_005514.7:c.900G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322996C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | YES | 12,23 | 57,593 | 57,7534 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 8,536585366 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Pro71=) | NM_005514.7:c.213G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324595C>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 11,63 | 16,2895 | 16,1718 | 81,6462 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 26,2195122 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Pro74=) | NM_005514.7:c.222G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324586C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 14,2 | 29,0403 | 34,9386 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 18,29268293 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Serl21=) | NM_005514.7:c.363C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324200G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 4,694 | 3,2343 | 3,3339 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ser26=) | NM_005514.7:c.78C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324730G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | YES | 11,68 | 1,3664 | 0,386 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 43,90243902 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ser336=) | NM_005514.7:c.1008T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31322888A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | YES | 4,089 | 77,1272 | 76,5535 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Ser48=) | NM_005514.7:c.144A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324664T>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 8,045 | 12,6143 | 15,7518 | 13,0793 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(lhr118=) | NM_005514.7:c.354C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324209G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | YES | YES | 7,178 | 0 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 15,85365854 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Thr158=) | NM_005514.7:c.474C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324089G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 11,16 | 3,6372 | 2,2775 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 26,2195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Thr162=) | NM_005514.7:c.486G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324077C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 13,48 | 1,5883 | 1,6212 | 40 | 97,56097561 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 25,6097561 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Thr162=) | NM_005514.7:c.486G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324077C>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 10,69 | 38,6657 | 41,2848 | 59,7864 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Thr252=) | NM_005514.7:c.756T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323233A>G | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,035 | 44,5239 | 43,3704 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Thr282=) | NM_005514.7:c.846A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323143T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,138 | 18,071 | 4,7174 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 0 | 9,146341463 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Thr55=) | NM_005514.7:c.165C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324643G>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 8,619 | 37,883 | 42,6687 | 62,1316 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 0 | 9,756097561 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Tyr123=) | NM_005514.7:c.369C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324194G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 0,212 | 23,9087 | 33,508 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 0 | 9,146341463 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Val285=) | NM_005514.7:c.855A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323134T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 13,32 | 17,7441 | 3,9315 | 34 | 82,92682927 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 24,3902439 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.(Val285=) | NM_005514.7:c.855A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323134T>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 2,456 | 0,0442 | 0,0437 | 82,2117 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 0 | 10,97560976 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala15Gly | NM_005514.7:c.44C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324892G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 7,314 | 39,9684 | 46,0736 | 57,8691 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala182Thr | NM_005514.7:c.544G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324019C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 11,22 | 0,2065 | 0,6119 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala223Val | NM_005514.7:c.668C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323321G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 7,797 | 9,7979 | 9,6858 | 32 | 78,04878049 | 0 | 19,51219512 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala329Thr | NM_005514.7:c.985G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322911C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 22,3 | 44,2739 | 43,5388 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala65Thr | NM_005514.7:c.193G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324615C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 13,89 | 9,9304 | 13,0787 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 15,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala93Thr | NM_005514.7:c.277G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324531C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 6,739 | 70,371 | 76,0648 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 17,07317073 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ala95Thr | NM_005514.7:c.283G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324525C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 11,07 | 0,0393 | 0,0016 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg103_Asn104insGlu | NM_005514.7:c.308_309insAGA | NC_000006.11:g.3132449931324500insTCT | Coding exon | Insertion | NO | YES | 16 | 39,02439024 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 10,97560976 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg103Thrfs*49 | NM_005514.7:c.306_307insAC | NC_000006.11:g.3132450131324502insGT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg106Alafs*45 | NM_005514.7:c.315delG | NC_000006.11:g.31324493delC | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 22,9 | 12,9825 | 9,353 | 12,9825 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg106Leu | NM_005514.7:c.317G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324491C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 5,414 | 7,4281 | 6,2526 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 26,2195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg155Ser | NM_005514.7:c.463C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324100G>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 8,954 | 41,3205 | 44,2724 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 26,2195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg169Leu | NM_005514.7:c.506G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324057C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 25 | 1,9414 | 1,8143 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 24,3902439 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg180Aspfs*35 | NM_005514.7:c.537_538insGA | NC_000006.11:g.3132402531324026insTC | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 16,81 | 14,1501 | 14,679 | 17,614 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg180Gln | NM_005514.7:c.539G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324024C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 11,86 | 0,1175 | 0,1105 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg180Glnfs*27 | NM_005514.7:c.539_540delGG | NC_000006.11:g.31324023_31324024delCC | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 22,6 | 15,8133 | 14,2816 | 15,8133 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 30 | 73,17073171 | 43,29268293 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg180Gly | NM_005514.7:c.538C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324025G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 4,17 | 0,4825 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg180Leu | NM_005514.7:c.539G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324024C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 7,935 | 50,2561 | 47,0553 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg180Trp | NM_005514.7:c.538C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324025G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,206 | 19,6659 | 17,8451 | 22,5899 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 24 | 58,53658537 | 39,02439024 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg181Glufs*33 | NM_005514.7:c.540delG | NC_000006.11:g.31324024delC | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 22 | 53,65853659 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 30,48780488 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg243Trp | NM_005514.7:c.727C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323262G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 29,5 | 7,5581 | 0,5349 | 7,5581 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 14,63414634 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg263Gly | NM_005514.7:c.787A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323202T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,04 | 24,272 | 5,5489 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 14,63414634 | 18,29268293 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Arg86Gly | NM_005514.7:c.256C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324552G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,669 | 3,2927 | 2,0834 | 3,5043 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn104_Leu105delinsMet | NM_005514.7:c.311_313delACC | NC_000006.11:g.31324495_31324497delGGT | Coding exon | Insertion/Deletion | NO | YES | 8,006 | 14,6059 | 10,4071 | 14,6072 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 2,43902439 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn104Ile | NM_005514.7:c.311A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324497T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 6,927 | 0,0056 | 0,0006 | 76,0583 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn104Serfs*46 | NM_0055147:c.311_314delACCT | NC_000006.11:g.31324494_31324497delAGGT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 21,5 | 0,0013 | 0,0013 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn104Thr | NM_005514.7:c.311A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324497T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 5,825 | 6,929 | 4,7476 | 8 | 19,51219512 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 45,12195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn104Thrfs*34 | NM_005514.7:c.311_312delAC | NC_000006.11:g.31324496_31324497delGT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn104Thrfs*47 | NM_005514.7:c.311delA | NC_000006.11:g.31324498delT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 9,509 | 3,2488 | 3,3109 | 3,4633 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 44,51219512 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn87Asp | NM_005514.7:c.259A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324549T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 1,09 | 33,9071 | 35,5134 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 2,43902439 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asn87Lys | NM_005514.7:c.261C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324547G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 12,57 | 34,0051 | 35,61 | 65,432 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp138Asn | NM_005514.7:c.412G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324151C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,007 | 45,4023 | 45,9411 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp138His | NM_005514.7:c.412G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324151C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,357 | 3,5677 | 3,6749 | 51,0258 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp201Asn | NM_005514.7:c.601G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323962C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 21,1 | 0,0014 | 0,0231 | 32 | 78,04878049 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 20,73170732 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp201Glu | NM_005514.7:c.603C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323960G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,014 | 57,6933 | 68,279 | 40,9375 | 35 | 85,36585366 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 23,7804878 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp201Lysfs*14 | NM_005514.7:c.600_601insAA | NC_000006.11:g.31323962_31323963insTT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 24,9 | 0,0726 | 0,0183 | 0,0726 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 21,34146341 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp54Gly | NM_005514.7:c.161A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324647T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 23,6 | 4,7592 | 3,6628 | 4,6675 | 35 | 85,36585366 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 23,7804878 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Asp98Tyr | NM_005514.7:c.292G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324516C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,533 | 59,3112 | 61,8419 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 21,34146341 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Cys349Ser | NM_005514.7:c.1046G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31322303C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | YES | 0,001 | 52,4683 | 52,5197 | 47,2634 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln120Glyfs*32 | NM_005514.7:c.357_358insGG | NC_000006.11:g.31324205_31324206insCC | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 25,7 | 7,0835 | 8,4468 | 7,0835 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 31 | 75,6097561 | 43,90243902 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln56Leu | NM_005514.7:c.167A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324641T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 25,1 | 10,1749 | 14,6787 | 89,3553 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 0 | 5,487804878 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln89Arg | NM_005514.7:c.266A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324542T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 2,645 | 3,8034 | 2,6479 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 16,46341463 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94* | NM_005514.7:c.280C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324528G>A | Coding exon | Nonsense | NO | YES | 0,7 | 0,001 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 20,73170732 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94Argfs*4 | NM_005514.7:c.281_282delAG | NC_000006.11:g.31324526_31324527delCT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 18,5 | 23,9284 | 3,2512 | 23,9405 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 16,46341463 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94Asnfs*58 | NM_005514.7:c.279_280insAA | NC_000006.11:g.3132452831324529insTT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 14,16 | 70,5354 | 76,1003 | 73,59 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94His | NM_005514.7:c.282G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324526C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 9,392 | 0,1118 | 0,0125 | 71,3835 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 30,48780488 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94Hisfs*4 | NM_005514.7:c.282_283delGG | NC_000006.11:g.3132452531324526delCC | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 22,8 | 69,6503 | 72,857 | 69,6503 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94Lys | NM_005514.7:c.280C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324528G>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,346 | 4,1499 | 3,7558 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94Pro | NM_005514.7:c.281A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324527T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 9,561 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 15,85365854 | |||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gln94Seifs*58 | NM_005514.7:c.279_280insTC | NC_000006.11:g.3132452931324530insAG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 14,16 | 4,0074 | 3,2488 | 4,1809 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu100Vol | NM_005514.7:c.299A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324509T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 11,74 | 1,2622 | 1,2118 | 98,5299 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 26,2195122 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu176Ala | NM_005514.7:c.527A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324036T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,327 | 0,2216 | 0,1532 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu176Vol | NM_005514.7:c.527A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324036T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 41,6419 | 43,5173 | 58,1054 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu187Ala | NM_005514.7:c.560A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324003T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 31,8706 | 32,8644 | 0,0339 | 32 | 78,04878049 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 24,3902439 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu187Gln | NM_005514.7:c.559G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324004C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,16 | 37,7301 | 39,6141 | 30,077 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 12,80487805 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu187Lys | NM_005514.7:c.559G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324004C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 2,834 | 31,973 | 32,8101 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu187Val | NM_005514.7:c.560A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324003T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,023 | 37,6498 | 39,5155 | 30,2167 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 2,43902439 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu197Lys | NM_005514.7:c.589G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323974C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 25,3 | 1,8855 | 1,1719 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu204Gln | NM_005514.7:c.610G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323953C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | YES | 0,021 | 65,4 | 72,4059 | 33,7911 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu299Lys | NM_005514.7:c.895G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323094C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | YES | 24,1 | 0,0182 | 0,0615 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 26,2195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu69Ala | NM_005514.7:c.206A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324602T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 5,248 | 0,0065 | 0,0015 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu69Argfs*8 | NM_005514.7:c.204delA | NC_000006.11:g.31324604delT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 14,13 | 17,5781 | 19,0359 | 19,445 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 26,2195122 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu69Aspfs*30 | NM_005514.7:c.206_207insC | NC_000006.11:g.31324601_31324602insG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 22,4 | 12,1956 | 11,5165 | 11,4642 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 14,02439024 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu69Aspfs*30 | NM_005514.7:c.206_207insT | NC_000006.11:g.31324601_31324602insA | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 22,4 | 2,6037 | 3,1117 | 2,4883 | 27 | 65,85365854 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 20,12195122 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu69Lys | NM_005514.7:c.205G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324603C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 7,692 | 9,5995 | 15,1153 | 48,4824 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 15,24390244 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu69Val | NM_005514.7:c.206A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324602T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 6,536 | 0,0033 | 0,0007 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 14,63414634 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glu70Ala | NM_005514.7:c.209A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324599T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 24,3 | 2,5646 | 2,9318 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Glyl07Alafs*33 | NM_005514.7:c.319_320insCTCC | NC_000006.11:g.3132448831324489insGGAG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 24,5 | 13,3328 | 10,7929 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 29,87804878 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gly107Alafs*45 | NM_005514.7:c.319_320insCC | NC_000006.11:g.3132448831324489insGG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 23,1 | 2,9093 | 3,419 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gly107Arg | NM_005514.7:c.319G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324489C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 5,228 | 7,2419 | 5,8869 | 87,6388 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gly107Cys | NM_005514.7:c.319G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324489C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 23,3 | 4,2489 | 4,4768 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 36 | 87,80487805 | 46,95121951 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Gly107Ilefs*46 | NM_005514.7:c.317_318insGATCG | NC_000006.11:g.3132449231324493insATCCG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 40 | 97,56097561 | 0 | 24,3902439 | |||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.His137Tyr | NM_005514.7:c.409C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324154G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,003 | 27,3148 | 26,549 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ile218Val | NM_005514.7:c.652A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323337T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 23,29 | 23,3893 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p. Ile90_Tyr91delinsAsn | NM_005514.7:c.269_271delTCT | NC_000006.11:g.3132453731324539delAGA | Coding exon | Insertion/Deletion | NO | YES | 11,3 | 3,8699 | 3,2439 | 15,7045 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 28,04878049 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ile90Asn | NM_005514.7:c.269T>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324539A>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,003 | 0,0986 | 0,207 | 99,353 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu105Argfs*46 | NM_005514.7:c.314delT | NC_000006.11:g.31324494delA | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 19,97 | 3,244 | 3,2546 | 6,5895 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu105del | NM_005514.7:c.314_316delTGC | NC_000006.11:g.31324493_31324495delCAG | Coding exon | Deletion | NO | YES | 13 | 31,70731707 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 42,07317073 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu105Pro | NM_005514.7:c.314T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324494A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 23,2 | 0,0032 | 0,0006 | 28,8938 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu105Profs*33 | NM_005514.7:c.314_315delTG | NC_000006.11:g.3132449331324494delCA | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu105Val | NM_005514.7:c.313C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324495G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 7,54 | 0,0014 | 0,0006 | 1,9518 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 9,756097561 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu119Arg | NM_005514.7:c.356T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324207A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 23,6 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 31,70731707 | |||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu119Ile | NM_005514.7:c.355C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324208G>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 24,1648 | 25,4092 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu119Phe | NM_005514.7:c.355C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324208G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,382 | 0 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 37,19512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu119Profs*19 | NM_005514.7:c.354_355delCC | NC_000006.11:g.31324209_31324210delGG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | YES | YES | 23,4 | 7,3031 | 8,6855 | 26 | 63,41463415 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 19,51219512 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu119Serfs*32 | NM_005514.7:c.355delC | NC_000006.11:g.31324210delG | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 20 | 48,7804878 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 19,51219512 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu17Val | NM_005514.7:c.49C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324887G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 22,6 | 25,3964 | 30,3761 | 72,5647 | 26 | 63,41463415 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 18,29268293 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Leu2Arg | NM_005514.7:c.5T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324931A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 6,401 | 59,0995 | 61,9014 | 60,3469 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Lys202Alafs*5 | NM_005514.7:c.604_605delAA | NC_000006.11:g.3132395831323959delTT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 23,2 | 0,2112 | 0,0185 | 0,2112 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 0 | 7,926829268 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Lys202Thr | NM_005514.7:c.605A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323958T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,005 | 74,1991 | 81,5323 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Lys292Glu | NM_005514.7:c.874A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323115T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,002 | 18,7265 | 5,9152 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Met4Thr | NM_005514.7:c.11T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324925A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 6,638 | 58,9501 | 61,9114 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser101_Leu102insArg | NM_005514.7:c.303_304insAGA | NC_000006.11:g.3132450431324505insTCT | Coding exon | Insertion | NO | YES | 14 | 34,14634146 | 0 | 8,536585366 | |||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser101Asn | NM_005514.7:c.302G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324506C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 4,204 | 22,1306 | 20,6561 | 24 | 58,53658537 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 15,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser101Asnfs*51 | NM_005514.7:c.301_302insAC | NC_000006.11:g.3132450631324507insGT | Coding exon | Frame Shift | NO | YES | 19 | 46,34146341 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 12,80487805 | ||||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser101Gly | NM_005514.7:c.301A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324507T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,918 | 4,5549 | 3,7244 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 0 | 10,97560976 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser121Arg | NM_005514.7:c.363C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324200G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,085 | 65,3352 | 70,9502 | 30,6883 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser121Asn | NM_005514.7:c.362G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324201C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,004 | 3,1026 | 3,2685 | 2,1554 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 0 | 12,80487805 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser121Cys | NM_005514.7:c.361A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324202T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,002 | 1,0155 | 1,4367 | 96,8779 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 2,43902439 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser121Thr | NM_005514.7:c.362G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324201C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,002 | 6,9778 | 7,2488 | 87,43 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser14Trp | NM_005514.7:c.41C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324895G>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 23,7 | 27,5617 | 33,5403 | 70,4301 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 2,43902439 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser28Phe | NM_005514.7:c.83C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324725G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | YES | 0,0883 | 0,128 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 0 | 5,487804878 | |||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser35Ala | NM_005514.7:c.103T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324705A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 1,503 | 56,4428 | 63,6734 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 15,85365854 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser48Ala | NM_005514.7:c.142T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324666A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,21 | 46,7136 | 42,8675 | 24 | 58,53658537 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 23,17073171 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Ser48Thr | NM_005514.7:c.142T>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324666A>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,34 | 12,4078 | 16,3262 | 40,4096 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 14,63414634 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Thr118Ile | NM_005514.7:c.353C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324210G>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | YES | 17,54 | 21,3299 | 23,0229 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Thr162Lys | NM_005514.7:c.485C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324078G>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 13,4 | 6,451 | 4,1867 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 26,2195122 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Trp191Ser | NM_005514.7:c.572G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323991C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 8,923 | 9,7552 | 8,0324 | 90,2448 | 18 | 43,90243902 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 34,14634146 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr123Phe | NM_005514.7:c.368A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324195T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,886 | 0,3753 | 0,4723 | 99,5325 | 23 | 56,09756098 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 18,90243902 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr123Ser | NM_005514.7:c.368A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324195T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 14,75 | 0,091 | 0,4551 | 0,0011 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr140* | NM_005514.7:c.420C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324143G>T | Coding exon | Nonsense | NO | YES | 29,5 | 6,9791 | 5,5843 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr140Asp | NM_005514.7:c.418T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324145A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 14,0091 | 12,3637 | 14,0091 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 20,73170732 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr140Phe | NM_005514.7:c.419A>T | NC_CCCCC6.11:g.31324144T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 20,1943 | 19,0754 | 20,3351 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 10,36585366 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr140Ser | NM_005514.7:c.419A>C | NC_CCCCC6.11:g.31324144T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,001 | 19,2367 | 22,2731 | 19,5806 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,829268293 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr195His | NM_005514.7:c.583T>C | NC_CCCCC6.11:g.3132398CA>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 4,606 | 7,0066 | 7,5071 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,829268293 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr33Asp | NM_005514.7:c.97T>G | NC_CCCCC6.11:g.31324711A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,01 | 4,63 | 5,8449 | 8 | 19,51219512 | 0 | 4,87804878 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr33His | NM_005514.7:c.97T>C | NC_CCCCC6.11:g.31324711A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,027 | 16,8116 | 17,1135 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 14,63414634 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr91* | NM_005514.7:c.273C>G | NC_CCCCC6.11:g.31324535G>C | Coding exon | Nonsense | NO | YES | 35 | 0,001 | 0,0004 | 99,602 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr91_Lys92insMet | NM_005514.7:c.274_275insTGA | NC_000006.11:9.3132453431324535nsCAT | Coding exon | Insertion | NO | YES | 7,12 | 3,8577 | 2,7891 | 15 | 36,58536585 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 12,80487805 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr91Asn | NM_005514.7:c.271T>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324537A>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 2,907 | 0,0011 | 0,0038 | 99,5942 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr91Cys | NM_005514.7:c.272A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324536T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 6,514 | 14,551 | 15,5791 | 36,6813 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 10,36585366 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr91Phe | NM_005514.7:c.272A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324536T>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 8,641 | 29,4641 | 29,7045 | 18,8898 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Tyr91Ser | NM_005514.7:c.272A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324536T>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 8,067 | 31,3427 | 34,5332 | 9,8243 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 10,36585366 |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Val127Leu | NM_005514.7:c.379G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324184C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,011 | 4,683 | 10,0588 | 94,1052 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 12,80487805 |
| HLA-B | NP_Cl05505.2:p.Val272Met | NM_005514.7:c.814G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323175C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 25,7 | 0,0058 | 0,0011 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 12,80487805 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Val306le | NM_005514.7:c.916G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322980C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,039 | 44,7249 | 44,0241 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | ||
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Val36Met | NM_005514.7:c.106G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324702C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 17,12 | 49,5751 | 57,0086 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 16,46341463 | |
| HLA-B | NP_005505.2:p.Val9Leu | NM_005514.7:c.25G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324911C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 9,781 | 7,8903 | 9,3882 | 91,0713 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 38 | 92,68292683 | 48,17073171 |
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+27 *4+34delTGGGGTGG | NC_000006.11:g.31322224_31322231delACCCCACC | Intron | NO | YES | 3,004 | 4,2482 | 1,3615 | 4,4417 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4t27delT | NC_000006.11:g.31322229delA | Intron | NO | YES | 0,02 | 0,0011 | 0,0886 | 0,0011 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4t27T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31322229A>G | Intron | NO | YES | 0,159 | 19,4564 | 20,1396 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 8,536585366 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4t32 *4+35delTGGC | NC_000006.11:g.31322221_31322224delGCCA | Intron | NO | YES | 3,238 | 14,2031 | 16,9559 | 20,8299 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+32 *4+42delTGGCGGGTCTG | NC_000006.11:g.31322215_31322225delAGACCCGCCAC | Intron | NO | YES | 3,12 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 16,46341463 | |||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+32 *4+43delTGGCGGGTCTGG | NC_000006.11:g.31322215_31322226delAGACCCGCCACC | Intron | NO | YES | 6 | 14,63414634 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 4,87804878 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+32delT | NC_000006.11:g.31322224delA | Intron | NO | YES | 4,482 | 0,0945 | 0,5779 | 0,0945 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+32T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31322224A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 3,848 | 8,0337 | 14,5852 | 8,3692 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 25 | 60,97560976 | 39,02439024 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+35delC | NC_000006.11:g.31322221delG | Intron | NO | YES | 3,299 | 0,1394 | 2,2648 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+36G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322220C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 4,246 | 29,639 | 17,6763 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+39_*4+41delTCT | NC_000006.11:g.3132221531322217delAGA | Intron | NO | YES | 4,979 | 10,378 | 9,0655 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 8,536585366 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+39T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31322217A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 0,744 | 11,7196 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 7,926829268 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.*4+4C_*4+42delCÍG | NC_000006.11:g.3132221431322216delCAG | Intron | NO | YES | 4,552 | 0,0062 | 0,2049 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+41_*4+42delTG | NC_000006.11:g.3132221431322215delCA | Intron | NO | YES | 4,577 | 10,0843 | 3,0674 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 0 | 5,487804878 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+41T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31322215A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 1,314 | 0,0168 | 0,2244 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.*4+45G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322211C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 3,632 | 0,0081 | 0,0014 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 32 | 78,04878049 | 44,51219512 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C12+29G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322855C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 0,921 | 7,5948 | 7,4886 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 15,24390244 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C13-17A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31322459T>C | Intron | NO | YES | 15,15 | 26,5818 | 26,5702 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 0 | 6,097560976 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.1013-28G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31322470C>G | Intron | NO | YES | 0,535 | 84,6565 | 84,7442 | 15,2418 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C13-32C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31322474G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 2,029 | 0,1195 | 0,1253 | 0,1171 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C13-45C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31322487G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 1,101 | 10,2244 | 10,1143 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C45+15T>C | NC_000006.11:g.31322395A>G | Intron | NO | YES | 7,58 | 9,9476 | 9,7782 | 9,8715 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C45+43A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31322367T>G | Intron | NO | YES | 4,843 | 7,526 | 7,5566 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 8,536585366 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C45+8G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322402C>T | Intron | YES | YES | 10,81 | 26,6203 | 26,5963 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C46-37C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31322340G>T | Intron | NO | YES | 0,447 | 3,3586 | 3,3758 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 38 | 92,68292683 | 48,17073171 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.1C46-37C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31322340G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 1,072 | 7,7087 | 8,443 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.-18G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324953C>T | UTR | NO | YES | 2,871 | 59,8493 | 60,2889 | 60,9438 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.-2CG>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324955C>T | UTR | NO | YES | 9,762 | 7,4508 | 5,791 | 7,673 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 0 | 4,268292683 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.343+17C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324448G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 8,14 | 9,2551 | 8,4386 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.343+5CT>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324415A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 5,211 | 15,2245 | 15,1806 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_CC5514.7:c.344-1CC>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324229G>C | Intron | YES | YES | 4,958 | 8,7411 | 10,4829 | 91,2589 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 29,87804878 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-16G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324235C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 9,304 | 1,9563 | 1,8634 | 1,9563 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 14,63414634 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-24G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324243C>A | Intron | NO | YES | 9,475 | 4,0708 | 6,0333 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-26delT | NC_000006.11:g.31324245delA | Intron | NO | YES | 7,813 | 0,0316 | 0,0059 | 0,0316 | 11 | 26,82926829 | 28 | 68,29268293 | 40,85365854 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-26T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324245A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 2,187 | 70,8559 | 79,3142 | 72,3828 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 8,536585366 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_j3C'5514.7:c.344-29_344-28insG | NC_000006.11:g.3132425231324253insC | Intron | NO | YES | 5,185 | 29,8479 | 30,6508 | 29,8507 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-36_344-35insGGGGC | NC_000006.11:g.31324270_31324271insCCCCG | Intron | NO | YES | 2,12 | 0,0453 | 1,3438 | 0,0453 | 8 | 19,51219512 | 0 | 4,87804878 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-42344-41insGGGGG | NC_000006.11:g.31324264_31324265insCCCCC | Intron | NO | YES | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-46344-45insTGGGC | NC_000006.11:g.31324268_313242699nsAGCCC | Intron | NO | YES | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-47_344-46insGGGGG | NC_000006.11:g.31324269_313242700nsCCCCC | Intron | NO | YES | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-48344-47insTCGGG | NC_000006.11:g.31324273_31324274insCGACC | Intron | NO | YES | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.344-8G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324227C>A | Intron | YES | YES | 9,536 | 16,2335 | 12,8601 | 16,2029 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.-3G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324938C>T | UTR | NO | YES | 3,754 | 4,574 | 3,95 | 4,4083 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.620-40A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323409T>C | Intron | NO | YES | 2,821 | 84,6702 | 84,7984 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.620-43T>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323412A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 9,442 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.620-45C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323414G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 3,456 | 2,5757 | 2,4822 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.620-47C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323416G>C | Intron | NO | YES | 0,817 | 9,1626 | 9,3164 | 90,9516 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 34 | 82,92682927 | 45,73170732 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.-6G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324941C>T | UTR | NO | YES | 7,363 | 1,8921 | 1,7678 | 1,9372 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.73+11_73+12insA | NC_000006.11:g.3132485131324852insT | Intron | NO | YES | 8,95 | 1,4629 | 1,6387 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.73+11_73+12insG | NC_000006.11:g.31324854_31324855insC | Intron | NO | YES | 8,95 | 37,1184 | 42,2209 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.73+16G>C | NC_000006.11:g.31324847C>G | Intron | NO | YES | 9,718 | 25,384 | 27,2645 | 26,0563 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.73+33C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324830G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 7,984 | 61,7311 | 65,8285 | 63,1271 | 4 | 9,756097561 | 0 | 2,43902439 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.73+34C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324829G>C | Intron | NO | YES | 7,021 | 61,0417 | 64,3156 | 62,1829 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.73+43C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324820G>T | Intron | NO | YES | 3,93 | 3,9893 | 4,092 | 4,3354 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 0 | 12,80487805 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-10_749insTG | NC_000006.11:g.31324743_31324744insCA | Intron | YES | YES | 8,688 | 3,7915 | 2,9408 | 3,8248 | 40 | 97,56097561 | 0 | 24,3902439 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-15C>A | NC_000006.11:g.31324749G>T | Intron | NO | YES | 8,48 | 6,4129 | 1,2942 | 6,4129 | 38 | 92,68292683 | 0 | 23,17073171 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-16C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324750G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 11,98 | 1,31 | 2,9103 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 7,926829268 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-22C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324756G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 13,91 | 4,2382 | 3,4719 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-30G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324764C>A | Intron | NO | YES | 14,05 | 3,5534 | 3,3596 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-3delC | NC_000006.11:g.31324741delG | Intron | YES | YES | 9,822 | 2,5959 | 26 | 63,41463415 | 0 | 15,85365854 | |||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-42G>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324776C>A | Intron | NO | YES | 9,736 | 0,7512 | 0,1388 | 0,7512 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-7C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324741G>C | Intron | YES | YES | 15,47 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-7C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324741G>A | Intron | YES | YES | 8,956 | 0,9247 | 0,1403 | 0,9247 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-8_74-6delACC | NC_000006.11:g.31324741_31324743delGTG | Intron | YES | YES | 7,955 | 3,6015 | 2,8825 | 3,6015 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-8_74-7delAC | NC_000006.11:g.31324742_31324743delTG | Intron | YES | YES | 8 | 19,51219512 | 0 | 4,87804878 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-8A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324742T>C | Intron | YES | YES | 6,55 | 81,8712 | 84,3621 | 82,3537 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-8A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324742T>A | Intron | YES | YES | 11,09 | 0,0177 | 0,0092 | 0,0166 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 12,19512195 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-8delA | NC_000006.11:g.31324742delT | Intron | YES | YES | 6,414 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 14,63414634 | |||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-9_74-7delCACinsTG | NC_000006.11:g.31324741_31324743delGTGinsCA | Intron | YES | YES | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-9C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31324743G>C | Intron | YES | YES | 7,618 | 0,8695 | 0,8713 | 98,789 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-9C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31324743G>A | Intron | YES | YES | 9,199 | 0,0014 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.74-9delC | NC_000006.11:g.31324743delG | Intron | YES | YES | 8,447 | 33 | 80,48780488 | 0 | 20,12195122 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+22C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323072G>C | Intron | NO | YES | 2,2 | 0,0151 | 0,093 | 0,0151 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+25A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323069T>C | Intron | NO | YES | 5,464 | 0,6167 | 0,4186 | 0,6167 | 19 | 46,34146341 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 27,43902439 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+27C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323067G>C | Intron | NO | YES | 5,848 | 0,6385 | 0,4195 | 0,6385 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+29C>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323065G>C | Intron | NO | YES | 6,588 | 14,5771 | 13,9235 | 85,2636 | 0 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,219512195 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+44895+45insTGAGCCCTTCT | NC_000006.11:g.3132304931323050insAGAAGGGCTCA | Intron | NO | YES | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+44895+45insTGATCCCTTCT | NC_000006.11:g.3132304931323050insAGAAGGGATCA | Intron | NO | YES | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+45895+46ÍnsAAGTCCTG | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGGACTTC | Intron | NO | YES | 14,66 | 0,0643 | 0,0911 | 0,0643 | 13 | 31,70731707 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,146341463 | ||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+45895+46insCAGCCCTTCTG | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAAGGGCTGC | Intron | NO | YES | 6 | 14,63414634 | 0 | 3,658536585 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+45895+46insTAGCCCTGCTG | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGCAGGGCTAC | Intron | NO | YES | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+45895+46insTAGCCCTTCTG | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAAGGGCTAC | Intron | NO | YES | 24 | 58,53658537 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 29,26829268 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+46895+47insCGCCCTTCTGG | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAAGGGCGCC | Intron | NO | YES | 19 | 46,34146341 | 9 | 21,95121951 | 22,56097561 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+46G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323048C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 15,28 | 0,85 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 0 | 9,756097561 | |||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.895+47896-46insTCCCTTCTGGA | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAAGGGATCC | Intron | NO | YES | 0,0004 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-12C>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323012G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 7,537 | 17,7809 | 17,903 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-20A>G | NC_000006.11:g.31323020T>C | Intron | NO | YES | 11,09 | 25,899 | 26,3527 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-26896-25insTGAGGCTTGGAGGTCAGGGC | NC_000006.11:g.31323034_31323035insTCCAAGCCTCAGCCCTGACC | Intron | NO | YES | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-27G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323027C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 12,6 | 1,3617 | 1,2155 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-35G>A | NC_000006.11:g.31323035C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 15,39 | 0 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 2,43902439 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-36A>C | NC_000006.11:g.31323036T>G | Intron | NO | YES | 15,31 | 0,0019 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 1,829268293 | ||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-36A>T | NC_000006.11:g.31323036T>A | Intron | NO | YES | 16,39 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | ||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-40896-39insTGGAGCCCTTC | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAAGGGCTCC | Intron | NO | YES | 12,94 | 48,4352 | 48,1478 | 48,9402 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-43896-42insGTCTGGAGCCC | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGACGGGCTCC | Intron | NO | YES | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-44896-43insATTCTGGAGCC | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAATGGCTCC | Intron | NO | YES | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-45896-44insACTTCTGGAGC | NC_000006.11:g.3132304931323050insAGAAGTGCTCC | Intron | NO | YES | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||||||
| HLA-B | NM_005514.7:c.896-46896-45insACCTTCTGGAG | NC_000006.11:g.31323049_31323050insAGAAGGTCTCC | Intron | NO | YES | 16 | 39,02439024 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 10,97560976 | ||||||
| NUDT15 | NM_018283.3:c.*7G>A | NC_000013.10:g.48619942G>A | UTR | NO | NO | 0,33 | 6,624 | 6,7361 | 6,4937 | 29 | 70,73170732 | 0 | 17,68292683 | |||
| NUDT15 | NM_018283.3:c.158+52158+53insGGGGCGTGCGCAGAGGGACGATCTC | NC_000013.10:g.4861209248612093insGGGGCGTGCGCAGAGGGACGATCTC | Intron | NO | NO | 1,513 | 4,101 | 4,2305 | 4,1031 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 0 | 7,317073171 | |||
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.(Leu191=) | NM_006446.4:c.571T>C | NC_000012.11:g.21331599T>C | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 0,006 | 52,6046 | 52,195 | 51,9758 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.(Phel99=) | NM_006446.4:c.597C>T | NC_000012.11:g.21331625C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 12,16 | 38,5138 | 38,9939 | 38,6343 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 19,51219512 |
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.(Ser137=) | NM_006446.4:c.411G>A | NC_000012.11:g.21329761G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 6,028 | 11,2778 | 11,0057 | 11,0351 | 10 | 24,3902439 | 26 | 63,41463415 | 37,80487805 |
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.Asn130Asp | NM_006446.4:c.388A>G | NC_000012.11:g.21329738A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 0,002 | 47,9486 | 47,9938 | 8 | 19,51219512 | 0 | 4,87804878 | ||
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.Leu643Phe | NM_006446.4:c.1929A>C | NC_000012.11:g.21391976A>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 3,415 | 4,6322 | 4,5844 | 4,6241 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 26,82926829 |
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.Pro155Thr | NM_006446.4:c.463C>A | NC_000012.11:g.21329813C>A | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 2,73 | 11,6632 | 11,3856 | 11,4573 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 32,92682927 |
| SLCO1B1 | NP_006437.3:p.Val174Ala | NM_006446.4:c.521T>C | NC_000012.11:g.21331549T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 22,9 | 12,9434 | 13,3191 | 12,7777 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1682+7A>C | NC_000012.11:g.21370244A>C | Intron | YES | NO | 13,09 | 5 | 12,19512195 | 0 | 3,048780488 | ||||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+261747+38delAAAAAAAAATATA | NC_000012.11:g.21375324_21375336delAAAAAAAAATATA | Intron | NO | NO | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+33A>T | NC_000012.11:g.21375331A>T | Intron | NO | NO | 3,677 | 12 | 29,26829268 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 32,92682927 | |||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+341747+42delATATATATA | NC_000012.11:g.21375332_21375340delATATATATA | Intron | NO | NO | 29 | 70,73170732 | 6 | 14,63414634 | 25 | ||||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+351747+37delTAT | NC_000012.11:g.21375333_21375335delTAT | Intron | NO | NO | 9,537 | 0,0977 | 29 | 70,73170732 | 0 | 17,68292683 | |||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+351747+39delTATAT | NC_000012.11:g.21375333_21375337delTATAT | Intron | NO | NO | 9,339 | 0,014 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+35T>A | NC_000012.11:g.21375333T>A | Intron | NO | NO | 8,75 | 14,5833 | 12,3148 | 14,8936 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+39T>A | NC_000012.11:g.21375337T>A | Intron | NO | NO | 7,347 | 0,2865 | 2,3016 | 0,2865 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 35,97560976 | ||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+41T>A | NC_000012.11:g.21375339T>A | Intron | NO | NO | 3,377 | 0,5593 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 23 | 56,09756098 | 38,41463415 | ||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+43T>A | NC_000012.11:g.21375341T>A | Intron | NO | NO | 4,076 | 0,2046 | 16 | 39,02439024 | 21 | 51,2195122 | 35,36585366 | ||||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1747+9A>G | NC_000012.11:g.21375307A>G | Intron | YES | NO | 11,87 | 5,2566 | 10,1819 | 4,5991 | 20 | 48,7804878 | 7 | 17,07317073 | 20,73170732 | ||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.1865+4846T>C | NC_000012.11:g.21382619T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 1,565 | 21,0258 | 21,9249 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 12,80487805 | |||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.359+23_359+24insA | NC_000012.11:g.2132766621327667insA | Intron | NO | NO | 9,211 | 40,0171 | 42,1978 | 5,758 | 17 | 41,46341463 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 12,80487805 | ||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.359+23_359 +24insAA | NC_000012.11:g.2132766621327667insAA | Intron | NO | NO | 9,108 | 9,0865 | 9,2002 | 44,9076 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 0 | 0,609756098 | |||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.481+1G>T | NC_000012.11:g.21329832G>T | Intron | YES | NO | 22,7 | 0,2889 | 0,2997 | 0,314 | 3 | 7,317073171 | 0 | 1,829268293 | |||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.727+33C>T | NC_000012.11:g.21331987C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 2,492 | 40,6972 | 40,4735 | 40,2466 | 2 | 4,87804878 | 0 | 1,219512195 | |||
| SLCO1B1 | NM_006446.4:c.-910G>A | NC_000012.11:g.21283322G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 6,3214 | 5,4713 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 1 | 2,43902439 | 9,756097561 | ||||
| TPMT | NP_000358.1:p.(lle158=) | NM_000367.3:c.474C>T | NC_000006.11:g.18139214G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 14,07 | 76,3337 | 76,3961 | 76,2927 | 22 | 53,65853659 | 14 | 34,14634146 | 30,48780488 |
| TPMT | NP_000358.1:p.Ala154Thr | NM_000367.3:c.460G>A | NC_000006.11:g.18139228C>T | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 28,4 | 2,7492 | 2,7671 | ||||||
| TPMT | NP_000358.1:p.Ala80Pro | NM_000367.3:c.238G>C | NC_000006.11:g.18143955C>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | YES | YES | 29,5 | 0,1381 | 0,1685 | 99,8586 | |||||
| TPMT | NP_000358.1:p.Tyr240Cys | NM_000367.3:c.719A>G | NC_000006.11:g.18130918T>C | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | YES | 28,3 | 3,6689 | 3,7185 | ||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.141-10delT | NC_000006.11:g.18148166delA | Intron | YES | NO | 0,451 | 40,6003 | 19,7605 | 0,138 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.233+35C>T | NC_000006.11:g.18148019G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 4,774 | 52,0288 | 52,5022 | 52,0839 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.367-17delT | NC_000006.11:g.18139973delA | Intron | NO | NO | 3,202 | 65,2649 | 58,4255 | 0,0057 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.367-25T>A | NC_000006.11:g.18139973A>T | Intron | NO | NO | 0,019 | 1,3037 | 1,1009 | ||||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.367-27_367-26delAA | NC_000006.11:g.18139984_18139985delTT | Intron | NO | NO | 1,777 | 5,3655 | 5,6909 | 5,4753 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.580+14delG | NC_000006.11:g.18134023delC | Intron | NO | NO | 0,167 | 1,266 | 0,1178 | 1,266 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.580+14G>T | NC_000006.11:g.18134021C>A | Intron | NO | NO | 1,345 | 61,1539 | 66,4879 | 61,0312 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.580+26_580+27insT | NC_000006.11:g.18134020_18134021insA | Intron | NO | NO | 0,788 | 51,2875 | 55,8348 | 41,7252 | |||||||
| TPMT | NM_000367.3:c.580+26_580+27insTT | NC_000006.11:g.18134020_18134021insAA | Intron | NO | NO | 0,726 | 6,3537 | 6,3233 | 51,3512 | |||||||
| UGT1A1 | NP_000454.1:p.His203_Lys211delinsGln | NM_000463.2:c.609_632del | NC_000002.11:g.234669542234669565del | Coding exon | Insertion/Deletion | NO | NO | |||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NP_000454.1:p.Thr168Ala | NM_000463.2:c.502A>G | NC_000002.11:g.234669435A>G | Coding exon | Nonsynonymous | NO | NO | 12,11 | 0,0008 | 0,0014 | 0,0008 | |||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.*211T>C | NC_000002.11:g.234681416T>C | UTR | NO | NO | 0,737 | 74,7718 | 75,2396 | ||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.*339G>C | NC_000002.11:g.234681544G>C | UTR | NO | NO | 0,051 | 81,2089 | 82,1086 | ||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.*440G>C | NC_000002.11:g.234681645G>C | UTR | NO | NO | 1,174 | 73,3231 | 74,5008 | ||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-1352A>C | NC_000002.11:g.234667582A>C | Intron | NO | NO | 2,587 | 51,6751 | |||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-2951A>G | NC_000002.11:g.234665983A>G | Intron | NO | NO | 5,241 | 35,4615 | |||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-3152G>A | NC_000002.11:g.234665782G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 29,971 | 30,2117 | |||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-3275T>G | NC_000002.11:g.234665659T>G | Intron | NO | YES | 54,8473 | ||||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-364C>T | NC_000002.11:g.234668570C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 4,544 | 36,3619 | |||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-40_-39insTA | NC_000002.11:g.234668894234668895insTA | Intron | NO | YES | 6,723 | 34,6576 | 32,528 | ||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.-41_-40delTA | NC_000002.11:g.234668893_234668894delTA | Intron | NO | YES | 7,661 | 2,2006 | |||||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.996+18C>T | NC_000002.11:g.234675829C>T | Intron | NO | NO | 5,081 | 1,1561 | 1,2209 | 1,2791 | |||||||
| UGT1A1 | NM_000463.2:c.997-37T>C | NC_000002.11:g.234676458T>C | Intron | NO | NO | 5,189 | 3,4911 | 3,7776 | 3,4873 | |||||||
| VKORC1 | NP_076869.1:p.(Arg12=) | NM_024006.5:c.36G>A | NC_000016.9:g.31106015C>T | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | NO | 15,25 | 1,7664 | 1,5078 | 1,7148 | |||||
| VKORC1 | NP_076869.1:p.(Leu120=) | NM_024006.5:c.358C>T | NC_000016.9:g.31102589G>A | Coding exon | Synonymous | NO | YES | 11,89 | 1,9094 | 1,9988 | 2,0719 | |||||
| VKORC1 | NM_001311311.1:c.284-6_284-5insT | NC_000016.9:g.3110420131104202insA | Intron | YES | NO | 6,408 | 14,9733 | 16,1791 | 31,3233 | |||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.-1639G>A | NC_000016.9:g.31107689C>T | Intron | NO | YES | 32,5975 | 35,5631 | |||||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.173+324T>G | NC_000016.9:g.31105554A>C | Intron | NO | YES | 0,371 | 19,1899 | 18,9878 | 18,7661 | |||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.173+525C>T | NC_000016.9:g.31105353G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 7,872 | 16,7808 | 9,365 | ||||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.174-136C>T | NC_000016.9:g.31104878G>A | Intron | NO | YES | 10,42 | 32,6143 | 35,5831 | ||||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.-1877A>G | NC_000016.9:g.31107927T>C | Intron | NO | YES | 10,5002 | ||||||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.283+124G>C | NC_000016.9:g.31104509C>G | Intron | NO | YES | 5,156 | 37,492 | 41,6334 | ||||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.283+837T>C | NC_000016.9:g.31103796A>G | Intron | NO | YES | 8,857 | 64,309 | 60,9625 | ||||||||
| VKORC1 | NM_024006.5:c.-4931C>T | NC_000016.9:g.31110981G>A | Intron | NO | NO | 57,5756 | 52,5559 |
An analysis of clinically actionable alleles, grouped by gene and by individual, showed that all the subjects carried alleles of clinical interest in at least one of the 18 genes studied, with a mean of 4.02 ± 1.68 genes and a maximum number of seven genes; 4.8% of patients were carriers of clinically actionable alleles in one gene, 14.6% in two genes, 22% in three genes, 22% in four genes, 14.6% in five genes, 12.2% in six genes and 9.8% in seven genes.
The analysis of clinically actionable alleles grouped by gene (Figure 1) showed that over 50% of subjects carried alleles of clinical interest in the VKORC1, CYP4F2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP2B6 genes; between 15 and 50% of subjects carried such alleles in the UGT1A1, SLCO1B1, CYP2C9 and TPMT genes, and between 2 and 15% carried them in the HLA-B, CYP3A5, HLA-A and DPYD genes. None of the patients carried the RYR1, CACNA1S, G6PD, F5 or NUDT15 genes.
Distribution of pharmacogenetic phenotypes in the population and their potential influence (clinical actionability) on treatmentTable 1 shows the pharmacogenetic categories or phenotypes identified in the population. The identified genotypes, together with their frequency in the studied population, are shown in Table 2 in the Annex. Clinical guidelines establish prescription recommendations or strategies for specific medications within each one of these pharmacogenetic categories or phenotypes. A total of 75 different drugs were found to be discussed in the CPIC, DPWG, CPNDS guidelines; 63 of them (84%) appear to be potentially affected by one of the genetic variants identified in the sample.
Distribution of pharmacogenetic phenotypes in the analyzed genes
| Gene | Category | Nr (%) | Smith et al.30 | McInnes et al.7 (Eur) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CACNA1S | Negative (MH susceptibility) | 41 (100) | 667 (100) | |
| Intermediate metabolizer | 15 (36.6) | 247 (37) | 157,574 (35.3) | |
| CYP2B6 | Normal metabolizer | 21 (51.2) | 355 (53) | 235,044 (52.6) |
| Rapid metabolizer | 5 (12.2) | 65 (10) | 10,474 (2.3) | |
| Intermediate metabolizer | 14 (34.1) | 186 (29) | 116,100 (26) | |
| CYP2C19 | Normal metabolizer Rapid metabolizer |
|
|
|
| Ultrarapid metabolizer | 3 (7.3) | 27 (4) | 20,788 (4.7) | |
| CYP2C9 | Intermediate metabolizer | 13 (31.7) | 218 (33) | 144,156 (32.3) |
| Normal metabolizer | 28 (68.3) | 434 (65) | 284,032 (63,6) | |
| Intermediate metabolizer | 19 (46.3) | 248 (37) | 113,670 (25.4)* | |
| CYP2D6 | Normal metabolizer Poor metabolizer |
|
| |
| Ultrarapid metabolizer | 1 (2.4) | 19 (3) | * | |
| CYP3A5 | Intermediate metabolizer | 5 (12.2) | 125 (19) | 5,683 (1.3) |
| Poor metabolizer | 36 (87.8) | 496 (74) | 436,556 (97.6) | |
| Intermediate metabolizer | 22 (53.7) | 95,254 (21.3)** | ||
| CYP4F2 | Normal metabolizer Poor metabolizer |
| 217,127 (48.6)** | |
| DPYD | Intermediate metabolizer | 1 (2.4) | 8 (1) | 30,181 (6.8) |
| Normal metabolizer | 40 (97.6) | 659 (99) | 416,050 (93.2) | |
| F5 | Negative (FVL) | 41 (100) | ||
| G6PD | Normal activity | 41 (100) | ||
| HLA-A | Negative | 38 (92.7) | ||
| Positive (HLA-A*31:01 het.) | 3 (7.3) | |||
| HLA-B | Negative | 37 (90,2) | ||
| Positive (HLA-B*58:01 het.) | 4 (9.8) | |||
| NUDT15 | Normal metabolizer | 41 (100) | 444,955 (99.4) | |
| RYR1 | Negative (HM susceptibility) | 41 (100) | 662 (99) | |
| Increased function | 1 (2.4) | 158 (24) | 120,720 (27) | |
| Normal function | 16 (39) | 495 (74) | 171,380 (38.3) | |
| SLCO1B1 | Normal function; increased function | 10 (24.4) | ||
| Poor function | 1 (2.4) | 14 (2) | 10,304 (2.3) | |
| Decreased function | 13 (31.7) | 83,552 (18.7) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | 2 (4.9) | 59 (9) | ||
| TPMT | Intermediate metabolizer; poor metabolizer | 5 (12.2) | ||
| Normal metabolizer | 34 (82.9) | 607 (91) | ||
| Intermediate metabolizer | 17 (41.5) | 204 (0)*** | ||
| UGT1A1 | Normal metabolizer | 21 (51.2) | 142,438 (31.8)*** | |
| Poor metabolizer | 1 (2.4) | *** | ||
| Rapid metabolizer | 1 (2.4) | *** | ||
| NP c.-1639G>A | 13 (31.7) | 274 (41) | 175,737 (39.3) | |
| VKORC1 | hom. c.-1639G>A | 5 (12.2) | 88 (13) | 62,474 (14) |
| het. c.-1639G>A | 23 (56.1) | 305 (46) | 209,357 (46.8) |
FVL: factor V Leiden; het.: heterozygous carrier; hom.: homozygous carrier; MH: malignant hyperthermia; NC: non-carrier.
Figure 2 shows the proportion of patients with actionable variants in the different treatment categories included in the clinical guidelines.
Apart from the SNV and INDEL variants usually considered in conventional techniques, 14 samples (34.15%) were found to contain CNVs in the CYP2D6 gene. Five samples carried heterozygous deletions (*5), three samples had heterozygous duplications (x2) and 7 samples possessed hybrid CYP2D6/2D7 tandem alleles. One of the samples presented with a deletion and a *36 hybrid; the remaining hybrids identified were of the *68 class.
Candidate variants identifiedBy recourse to the analysis described in Figure 3, a total of five variants were identified that had not been included in the previously described sets of clinically actionable variants (11.4% of all clinically actionable variants, present in 12.2% of subjects). These variants were CYP2C19 p.Arg125His / c.374G>A, CYP2C9 p.Pro33Ser / c.97C>T and p.Val153Ala / c.458T>C, CYP2D6 p.Tyr355Cys / c.1064A>G and DPYD p.Lys259Glu / c.775A>G. Table 3 in the Annex includes a more detailed description of these variants including their location in the gene and their population frequency according to the gnomAD database.
DiscussionThe present article describes the prevalence of clinically actionable pharmacogenetic variants and alleles in the genes most commonly covered by clinical guidelines as well as the prevalence of new candidate variants in those same genes. The study was carried out using a purpose-developed pharmacogenetic platform based on NGS technologies aimed at providing support to studies seeking to advance both clinical practice and scientific inquiry13. A cohort of 41 patients was analyzed, which corresponded to the accessible patients from whom genomic sequencing data had been obtained using the same platform. Patients with breast cancer in their first cycle of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were deemed to be an appropriate population (proof of concept) to test the implementation of this kind of screening in clinical practice as genetic studies could be added to other diagnostic tests in these patients, the results provided by genomic biomarkers possibly changing future therapeutic management.
This study has shown that pharmacogenetic variants of clinical interest in key genes are highly prevalent, and that the majority of individuals in the studied population exhibited multiple clinically actionable variants. This high prevalence was already reported by other authors such as Van Driest et al. who identified one such variant in the majority of individuals studied (98%)26. Bush et al., who used the eMERGE cohort with an NGS capture sequencing panel (PGRNseq), identified one or more level A actionable variants (CPIC) in 96.19% of all samples, with a median of two actionable variants per individual27. Likewise, McInnes et al., who analyzed a cohort of patients from the UK Biobank using a whole genome approach, identified one variant in 99.5% of individuals with a mean of 3.7 genes per individual containing clinically actionable variants7.
Table 1 shows that, for some genes such as SLCO1B1 or TPMT, variant combinations have been identified for which multiple classifications are possible. These ambiguous results, reported previously by other authors and present in other pharmacogenetic analysis platforms, are due to the fact that certain combinations of functional variants may be identified in the same or in different alleles therefore affecting one or both alleles of the gene21–23.
NGS massive sequencing technologies allow identification of rare variants that have not been described previously and that are not included in conventional genotyping platforms. Although these variants are extremely rare in isolation, when taken as a whole they are apt to affect a large number of individuals6,8. The role of these variants has been scarcely studied in the literature, with most of the information available being based on proofs of concept9,10. This study identified a total of five candidate variants in 41 subjects (i.e., in 12.2% of the sample) using an algorithm that takes into consideration the variant's allelic frequency, the location of the gene, any changes in the protein sequence, and the in silico bioinformatic prediction (CADD). The accuracy of the in silico bioinformatic predictor used (CADD) has been estimated at 84%28. In addition to displaying a phred-scaled CADD score above 20, these variants are considered deleterious by at least three additional bioinformatic predictors: SIFT, Poliphen-2 and DANN. The p.Lys259Glu/c.775A>G DPYD variant is included in the pharmVar database as due for classification and, with the exception of the variants above, the bioinformatic Poliphen-2 predictor classifies it as benign. We believe that these in silico results do not preclude the performance of confirmation studies. As regards the potential clinical application of the technology, these variants could result in a decrease in the genes’ activity and patients carrying them may benefit from a closer follow-up when prescribed a drug that may be affected. Furthermore, 17% of the population studied by McInnes et al. carried at least one deleterious variant of one of the 14 genes analyzed that was not included in the existing allelic definitions7. In the limited sample included in this analysis, the frequency of potentially deleterious rare variants vs. the already established ones was low (5 vs. 39), which contrasts with previous reports, which found rare variants to account for half of total variants27. Lastly, rare genetic variants could be the key for applying the information about the better biologically preserved genes, e.g., those coding for pharmacological targets, as the only variants identified for many of these genes are rare29.
This is one of the first studies to analyze the results of implementing a pharmacogenomics-specific NGS sequencing platform to support clinical and research activities. The PGRN (Pharmacogenomics Research Network), in collaboration with several US centers involved in the eMERGE-PGx pharmacogenomic sequencing implementation project, has developed a similar platform to the one presented here11,27. For these projects to be successful, multi-center studies are needed that generate a broader knowledge base. It is to be hoped that more centers can join this initiative and benefit from the use of this platform for clinical and research purposes.
When selecting the technology to be used for pharmacogenetic implementation, it is essential to take into consideration numerous factors, most of them related to the assets that must be available to the molecular biology laboratory of the participating center. At the same time, it must be remembered that the different technologies are complementary and the decision to prioritize one over another should be made based on the specific clinical condition of the patient. A detailed description of pharmacogenetic technologies may be found in van der Lee M et al.6. The Annex included here provide a detailed explanation of the reasons behind the choice of the technological approach used.
The main limitations of this study are its small sample size and the failure to validate the genomic findings identified by means of in vitro, ex vivo or in vivo, molecular functional studies and subsequently validate the genotype-phenotype correlation in the studied patients. Another limitation is the failure to obtain information about the pharmacological treatment that patients were on at the time of —or before— the study, which could have been influenced by the pharmacogenetic alleles identified. Nor was there any intervention made regarding prescription of the medication, or were the patients’ health outcomes analyzed to evaluate the therapeutic interventions or their clinical relevance. Although that was not one of the goals of the study and the clinical impact of the pharmacogenetic alleles studied has admittedly been well-described in the literature, such evaluations could be useful to clinically validate the platform. It is estimated that around 24% of the general population receive a medication affected by their genotype7. What is more, this prevalence could be even higher in patients with the characteristics of the subject included in this study.
FundingThis article was funded by an AII SEFF grant for hospital pharmacy research.
AcknowledgementsThe authors wish to thank the staff at the Hospital Pharmacy Department of the A Coruña Hospital who were in change of looking after the subjects of this study. A special thanks goes to Teresa Calleja Chuclá, María Mateos Salvador and Elena Fernández Gabriel.
We would also like to thank the Health in Code staff members, who contributed to the processing and analysis of the samples. A special thanks goes to the members of the pharmacogenetics team (Sara Santana, Maite García, Iria Gómez and Rosalía Peteiro), tue quality team (Dolores Salvado), the laboratory team (Lisi Santiago, Isaac Rosa, Raquel Calvo, Marta Neira, María del Pilar González and Luis Santomé) and the bioinformatics team (Andrea Grana, Roberto Noya, Pablo García, Pablo Cabaleiro and David de Uña).
Conflict of interestLuis Ramudo Cela is a member of the scientific committee at Health in Code. The other authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
Contribution to the scientific literature
The present study demonstrates the usefulness of implementing next generation sequencing-based pharmacogenomic processes in clinical practice with a view to identifying both common and rare clinically actionable variants not studied previously by conventional approaches.
When selecting the technology for implementing a pharmacogenetic approach, it is crucial to consider a series of factors, most of them dependent on the assets and resources available to the molecular biology laboratory where the testing will be carried out. It is also important to bear in mind that the different technologies are complementary, and the decision to prioritize one over another should be made on the basis of the patients’ clinical situation.
Our hospital was already using NGS technology for diagnostic studies, and had obtained a large volume of samples prior to the setting up of the pharmacogenetics panel used in the study. Moreover, the team of molecular biologists, IT specialists and physicians who participated in the study had already gained significant experience in the management of purpose-developed “tailor-made” panels, databases and bioinformatic algorithms. This made it easier to carry out the required NCS processing and to acquire enough affordable reagents to deal with the high volume of work involved. Also, the possibility of combining pharmacogenetic and diagnostic samples in one single sequencing pool makes it possible to work with smaller batches of pharmacogenetic samples without the risk of excessive sample accumulations (which is an important limitation to the use of dedicated processes and is particularly important for array rtPCR technologies, where sample volumes are typically low). Although the theoretical per-sample cost for array rtPCR procedures is lower than the sample cost for NGS procedures, when such factors are considered as the depreciation of new equipment, the development of new workflows, the extra cost of personalizing the arrays and the need to use a larger number of sample batches, the implementation of this technology usually turns out to be more disadvantageous than adapting an already-implemented NGS procedure. New process automation systems such as the Magnis NGS Prep System, or Agilent's Bravo Automated Liquid Handling Platform allow a reduction of NGS preparation times in the wet lab of up to 48 hours. Mean NGS response times in our center are of 3-5 weeks from the arrival of the sample (including bioinformatic data processing and preparation of the clinical report). Emergency clinical scenarios (e.g., DPYD studies prior to treatment with fluoropyrimidines) may be addressed with more targeted complementary technologies such as Sanger sequencing or low-scale rtPCR.
While NGS panels that include a set of genes of interest do not need to have their design updated following the publication of new variants of interest for those genes, targeted technologies require either updating their design with any non-included variant or applying a complementary technique to ensure the success of the study.
The strengths of the platform include the fact that the laboratory is UNE-EN ISO 15189 and CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) certified, both accreditations covering NGS pharmacogenetic procedures. In addition, the platform has been validated by comparative studies performed by institutions from different geographical areas (the College of American Pathologists [CAP]), the European Molecular Genetics Quality Network [EMQN]) and the Spanish Society of Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics (SEFFT). The platform could be used by centers wishing to outsource the process or may alternatively be implemented in centers that possess the required equipment.
Clinical actionability of the recommendations of pharmacogenetic clinical guidelines grouped by drug, gene, and phenotype (or genotype, if appropriate)
| Drug | Gene | Phenotype/genotype | CPIC | DPWG | CPNDS |
| Abacavir | HLA-B | Positive *57:01 Negative 15:01 | Yes | Yes No | |
| Acenocoumarol | VKORC1 | het. c.-1639G>A | No | Yes | |
| hom. c.-1639G>A | Conditional | ||||
| NC c.-1639G>A | Conditional | ||||
| Alopurinol | HLA-B | *58:01 negative | No | ||
| *58:01 positive | Si | ||||
| Amitriptyline | CYP2C19 | IM | Conditional | ||
| NM | No | ||||
| PM | Si | ||||
| RM | Si | ||||
| UM | Si | ||||
| CYP2D6 | IM | Si | Si | ||
| NM | No | No | |||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Aripiprazole | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Atazanavir | UGT1A1 | NM PM | No Yes | ||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| Atomoxetine | CYP2D6 | NM | Conditional | No | |
| PM | Conditional | Yes | |||
| UM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| DF | Yes | ||||
| Atorvastatin | SLCO1B1 | NF PF | No Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| NUDT15 | NM | No | No | ||
| Azathioprine | PM | Yes | Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| TPMT | NM | No | No | ||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Brexpiprazole | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| Capecitabine | DPYD | NM | No | No | |
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| Carbamazepine | HLA-A | 31:01 negative | No | No | |
| HLA-B | 31:01 positive | Yes | Yes | ||
| *15:02 negative | No | No | |||
| *15:02 negative | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Celecoxib | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | Yes | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| Citalopram | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| RM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| UM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Conditional | ||
| RM | Yes | Yes | |||
| Clomipramine | UM | Yes | Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | ||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| Clopidogrel | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| RM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| UM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| IM | Yes | Conditional | No | ||
| Codeine | CYP2D6 | NM PM | No Yes | No Yes | No Yes |
| UM | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| CACNA1S | MH negative | No | |||
| Desflurane | MH positive | Yes | |||
| RYR1 | MH negative | No | |||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Desipramine | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| NM | Yes | ||||
| Dexlansoprazole | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | ||
| RM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| NM | No | ||||
| CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | |||
| RM | Yes | ||||
| Doxepin | UM | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | ||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| Efavirenz | CYP2B6 | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| RM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| UM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Eliglustat | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| CACNA1S | MH negative | No | |||
| Enflurane | MH positive | Yes | |||
| RYR1 | MH negative | No | |||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | Yes | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| Escitalopram | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| RM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Flecainide | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Flucytosine | DPYD | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| Flucloxacillin | HLA-B | *57:01 negative | No | ||
| *57:01 positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| Fluorouracil | DPYD | NM | No | No | |
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Flurbiprofen | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Fluvoxamine | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| CYP2C9 | NM | No | |||
| Fosphenytoin | PM | Yes | |||
| HLA-B | *15:02 negative | No | |||
| *15:02 positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Haloperidol | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| CACNA1S | MH negative | No | |||
| Halothane | MH positive | Yes | |||
| RYR1 | MH negative | No | |||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Hydrocodone | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Conditional | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Ibuprofen | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Yes | ||
| RM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| Imipramine | UM | Yes | Conditional | ||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | ||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | No | ||||
| Irinotecan | UGT1A1 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| Isoflurane | CACNA1S RYR1 | MH negative | No | ||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| MH negative | No | ||||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| NM | Yes | No | |||
| Lansoprazole | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Conditional | |
| RM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Lornoxicam | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Meloxicam | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| NUDT15 | NM | No | No | ||
| Mercaptopurine | PM | Yes | Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| TPMT | NM | No | No | ||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| CACNA1S | MH negative | No | |||
| Methoxiflurane | MH positive | Yes | |||
| RYR1 | MH negative | No | |||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Metoprolol | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| Nortriptyline | CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | |
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| NM | Yes | No | |||
| Omeprazole | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Conditional | |
| RM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Ondansetron | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Conditional | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| Oxcarbazepine | HLA-B | *15:02 negative | No | ||
| *15:02 positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| NM | Yes | No | |||
| Pantoprazole | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Conditional | |
| RM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| Paroxetine | CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | |
| PM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| het. c.-1639G>A | No | ||||
| Phenprocoumon | VKORC1 | hom. c.-1639G>A | Yes | ||
| NC c.-1639G>A | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| CYP2C9 | NM | No | No | ||
| Phenytoin | HLA-B | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| *15:02 negative | No | ||||
| *15:02 positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Pimozide | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Piroxicam | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Propafenone | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| DA | Yes | ||||
| Rasburicase | G6PD | NA | No | ||
| VA | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Risperidone | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| Sertraline | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| RM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| UM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| CACNA1S | MH negative | No | |||
| Sevoflurane | MH positive | Yes | |||
| RYR1 | MH negative | No | |||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| DF | Yes | Yes | |||
| Simvastatin | SLCO1B1 | NF | No | No | |
| PF | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Siponimod | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| Succinylcholine | CACNA1S | MH negative | No | ||
| RYR1 | MH positive | Yes | |||
| MH negative | No | ||||
| MH positive | Yes | ||||
| Systemic estrogenic contraceptives | F5 | FVL negative | No | ||
| FVL positive | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| Tacrolimus | CYP3A5 | NM | Yes | Yes | |
| PM | No | No | |||
| IM | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Tamoxifen | CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | No |
| PM | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| UM | Conditional | Conditional | Conditional | ||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Tenoxicam | CYP2C9 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| NUDT15 | NM | No | No | ||
| Thioguanine | PM | Yes | Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | Yes | |||
| TPMT | NM | No | No | ||
| PM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| Tramadol | CYP2D6 | NM | No | No | |
| PM | Yes | Conditional | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| NM | No | ||||
| CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | |||
| RM | Yes | ||||
| Trimipramine | UM | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| CYP2D6 | NM | No | |||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Conditional | ||||
| Tropisetron | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Conditional | ||||
| UM | Yes | ||||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Venlafaxine | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional | ||||
| IM | Conditional | Conditional | |||
| NM | No | No | |||
| Voriconazole | CYP2C19 | PM | Yes | Yes | |
| RM | Yes | Yes | |||
| UM | Yes | Yes | |||
| IM | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| CYP2C9 | NM | Yes | No | Yes | |
| PM | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Warfarin | CYP4F2 | NM | No Yes | ||
| PM | |||||
| het. c.-1639G>A | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| VKORCl | hom. c.-1639G>A | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| NC c.-l639G>A | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| IM | Yes | ||||
| Zuclopenthixol | CYP2D6 | NM | No | ||
| PM | Yes | ||||
| UM | Conditional |
CPIC: Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium; CPNDS: Canadian Pharmacogenomics Network for Drug Safety; DA: decreased activity; DF: decreased function; DPWG: Royal Dutch Association for the Advancement of Pharmacy-Pharmacogenetics Working Group; FVL: factor V Leiden; het.: heterozygosis; hom.: homozygosis; IF: increased function; IM: intermediate metabolizer; MH: malignant hyperthermia; NA: normal activity; NC: non-carrier; NF: normal function; NM: normal metabolizer; PF: poor function; PM: poor metabolizer; RM: rapid metabolizer; UM: ultrarapid metabolizer; VA: variable activity.